cub::DeviceReduce#
-
struct DeviceReduce#
DeviceReduce provides device-wide, parallel operations for computing a reduction across a sequence of data items residing within device-accessible memory.
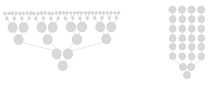
Overview#
A reduction (or fold) uses a binary combining operator to compute a single aggregate from a sequence of input elements.
Usage Considerations#
Dynamic parallelism. DeviceReduce methods can be called within kernel code on devices in which CUDA dynamic parallelism is supported.
Performance#
The work-complexity of reduction, reduce-by-key, and run-length encode as a function of input size is linear, resulting in performance throughput that plateaus with problem sizes large enough to saturate the GPU.
Public Static Functions
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename OutputIteratorT, typename ReductionOpT, typename T, typename NumItemsT>
static inline cudaError_t Reduce( - void *d_temp_storage,
- size_t &temp_storage_bytes,
- InputIteratorT d_in,
- OutputIteratorT d_out,
- NumItemsT num_items,
- ReductionOpT reduction_op,
- T init,
- cudaStream_t stream = 0
Computes a device-wide reduction using the specified binary
reduction_opfunctor and initial valueinit.Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
Does not support binary reduction operators that are non-commutative.
Provides “run-to-run” determinism for pseudo-associative reduction (e.g., addition of floating point types) on the same GPU device. However, results for pseudo-associative reduction may be inconsistent from one device to a another device of a different compute-capability because CUB can employ different tile-sizing for different architectures.
The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_out.When
d_temp_storageisnullptr, no work is done and the required allocation size is returned intemp_storage_bytes. See Determining Temporary Storage Requirements for usage guidance.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates a user-defined min-reduction of a device vector of
intdata elements.#include <cub/cub.cuh> // or equivalently <cub/device/device_reduce.cuh> // CustomMin functor struct CustomMin { template <typename T> __device__ __forceinline__ T operator()(const T &a, const T &b) const { return (b < a) ? b : a; } }; // Declare, allocate, and initialize device-accessible pointers for // input and output int num_items; // e.g., 7 int *d_in; // e.g., [8, 6, 7, 5, 3, 0, 9] int *d_out; // e.g., [-] CustomMin min_op; int init; // e.g., INT_MAX ... // Determine temporary device storage requirements void *d_temp_storage = nullptr; size_t temp_storage_bytes = 0; cub::DeviceReduce::Reduce( d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_out, num_items, min_op, init); // Allocate temporary storage cudaMalloc(&d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes); // Run reduction cub::DeviceReduce::Reduce( d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_out, num_items, min_op, init); // d_out <-- [0]
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (may be a simple pointer type)
OutputIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording the reduced aggregate (may be a simple pointer type)
ReductionOpT – [inferred] Binary reduction functor type having member
T operator()(const T &a, const T &b)T – [inferred] Data element type that is convertible to the
valuetype ofInputIteratorTNumItemsT – [inferred] Type of num_items
- Parameters:
d_temp_storage – [in] Device-accessible allocation of temporary storage. When
nullptr, the required allocation size is written totemp_storage_bytesand no work is done.temp_storage_bytes – [inout] Reference to size in bytes of
d_temp_storageallocationd_in – [in] Pointer to the input sequence of data items
d_out – [out] Pointer to the output aggregate
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)reduction_op – [in] Binary reduction functor
init – [in] Initial value of the reduction
stream – [in]
[optional] CUDA stream to launch kernels within. Default is stream0.
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename OutputIteratorT, typename ReductionOpT, typename T, typename NumItemsT, typename EnvT = ::cuda::std::execution::env<>>
static inline cudaError_t Reduce( - InputIteratorT d_in,
- OutputIteratorT d_out,
- NumItemsT num_items,
- ReductionOpT reduction_op,
- T init,
- EnvT env = {}
Computes a device-wide reduction using the specified binary
reduction_opfunctor and initial valueinit.Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
Does not support binary reduction operators that are non-commutative.
By default, provides “run-to-run” determinism for pseudo-associative reduction (e.g., addition of floating point types) on the same GPU device. However, results for pseudo-associative reduction may be inconsistent from one device to a another device of a different compute-capability because CUB can employ different tile-sizing for different architectures. To request “gpu-to-gpu” determinism, pass
cuda::execution::require(cuda::execution::determinism::gpu_to_gpu)as the env parameter. To request “not-guaranteed” determinism, passcuda::execution::require(cuda::execution::determinism::not_guaranteed)as the env parameter.The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_out.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates a user-defined min-reduction of a device vector of
intdata elements.auto op = cuda::std::plus{}; auto input = thrust::device_vector<float>{0.0f, 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f}; auto output = thrust::device_vector<float>(1); auto init = 0.0f; auto env = cuda::execution::require(cuda::execution::determinism::run_to_run); auto error = cub::DeviceReduce::Reduce(input.begin(), output.begin(), input.size(), op, init, env); if (error != cudaSuccess) { std::cerr << "cub::DeviceReduce::Reduce failed with status: " << error << std::endl; } thrust::device_vector<float> expected{6.0f};
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (may be a simple pointer type)
OutputIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording the reduced aggregate (may be a simple pointer type)
ReductionOpT – [inferred] Binary reduction functor type having member
T operator()(const T &a, const T &b)T – [inferred] Data element type that is convertible to the
valuetype ofInputIteratorTNumItemsT – [inferred] Type of num_items
EnvT – [inferred] Execution environment type. Default is
cuda::std::execution::env<>.
- Parameters:
d_in – [in] Pointer to the input sequence of data items
d_out – [out] Pointer to the output aggregate
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)reduction_op – [in] Binary reduction functor
init – [in] Initial value of the reduction
env – [in]
[optional] Execution environment. Default is
cuda::std::execution::env{}.
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename OutputIteratorT, typename NumItemsT, typename EnvT = ::cuda::std::execution::env<>>
static inline cudaError_t Sum( - InputIteratorT d_in,
- OutputIteratorT d_out,
- NumItemsT num_items,
- EnvT env = {}
Computes a device-wide sum using the addition (
+) operator.Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
Uses
0as the initial value of the reduction.Does not support
+operators that are non-commutative.Provides “run-to-run” determinism for pseudo-associative reduction (e.g., addition of floating point types) on the same GPU device. However, results for pseudo-associative reduction may be inconsistent from one device to a another device of a different compute-capability because CUB can employ different tile-sizing for different architectures. To request “gpu-to-gpu” determinism, pass
cuda::execution::require(cuda::execution::determinism::gpu_to_gpu)as the env parameter. To request “not-guaranteed” determinism, passcuda::execution::require(cuda::execution::determinism::not_guaranteed)as the env parameter.The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_out.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates a user-defined min-reduction of a device vector of
intdata elements.auto input = thrust::device_vector<float>{0.0f, 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f}; auto output = thrust::device_vector<float>(1); auto env = cuda::execution::require(cuda::execution::determinism::run_to_run); auto error = cub::DeviceReduce::Sum(input.begin(), output.begin(), input.size(), env); if (error != cudaSuccess) { std::cerr << "cub::DeviceReduce::Sum failed with status: " << error << std::endl; } thrust::device_vector<float> expected{6.0f};
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (may be a simple pointer type)
OutputIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording the reduced aggregate (may be a simple pointer type)
NumItemsT – [inferred] Type of num_items
EnvT – [inferred] Execution environment type. Default is
cuda::std::execution::env<>.
- Parameters:
d_in – [in] Pointer to the input sequence of data items
d_out – [out] Pointer to the output aggregate
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)env – [in]
[optional] Execution environment. Default is cuda::std::execution::env{}.
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename OutputIteratorT, typename NumItemsT>
static inline cudaError_t Sum( - void *d_temp_storage,
- size_t &temp_storage_bytes,
- InputIteratorT d_in,
- OutputIteratorT d_out,
- NumItemsT num_items,
- cudaStream_t stream = 0
Computes a device-wide sum using the addition (
+) operator.Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
Uses
0as the initial value of the reduction.Does not support
+operators that are non-commutative.Provides “run-to-run” determinism for pseudo-associative reduction (e.g., addition of floating point types) on the same GPU device. However, results for pseudo-associative reduction may be inconsistent from one device to a another device of a different compute-capability because CUB can employ different tile-sizing for different architectures.
The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_out.When
d_temp_storageisnullptr, no work is done and the required allocation size is returned intemp_storage_bytes. See Determining Temporary Storage Requirements for usage guidance.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates the sum-reduction of a device vector of
intdata elements.#include <cub/cub.cuh> // or equivalently <cub/device/device_reduce.cuh> // Declare, allocate, and initialize device-accessible pointers // for input and output int num_items; // e.g., 7 int *d_in; // e.g., [8, 6, 7, 5, 3, 0, 9] int *d_out; // e.g., [-] ... // Determine temporary device storage requirements void *d_temp_storage = nullptr; size_t temp_storage_bytes = 0; cub::DeviceReduce::Sum( d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_out, num_items); // Allocate temporary storage cudaMalloc(&d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes); // Run sum-reduction cub::DeviceReduce::Sum(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_out, num_items); // d_out <-- [38]
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (may be a simple pointer type)
OutputIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording the reduced aggregate (may be a simple pointer type)
NumItemsT – [inferred] Type of num_items
- Parameters:
d_temp_storage – [in] Device-accessible allocation of temporary storage. When
nullptr, the required allocation size is written totemp_storage_bytesand no work is done.temp_storage_bytes – [inout] Reference to size in bytes of
d_temp_storageallocationd_in – [in] Pointer to the input sequence of data items
d_out – [out] Pointer to the output aggregate
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)stream – [in]
[optional] CUDA stream to launch kernels within. Default is stream0.
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename OutputIteratorT, typename NumItemsT>
static inline cudaError_t Min( - void *d_temp_storage,
- size_t &temp_storage_bytes,
- InputIteratorT d_in,
- OutputIteratorT d_out,
- NumItemsT num_items,
- cudaStream_t stream = 0
Computes a device-wide minimum using the less-than (
<) operator.Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
Uses
cuda::std::numeric_limits<T>::max()as the initial value of the reduction.Does not support
<operators that are non-commutative.Provides “run-to-run” determinism for pseudo-associative reduction (e.g., addition of floating point types) on the same GPU device. However, results for pseudo-associative reduction may be inconsistent from one device to a another device of a different compute-capability because CUB can employ different tile-sizing for different architectures.
The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_out.When
d_temp_storageisnullptr, no work is done and the required allocation size is returned intemp_storage_bytes. See Determining Temporary Storage Requirements for usage guidance.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates the min-reduction of a device vector of
intdata elements.#include <cub/cub.cuh> // or equivalently <cub/device/device_reduce.cuh> // Declare, allocate, and initialize device-accessible pointers // for input and output int num_items; // e.g., 7 int *d_in; // e.g., [8, 6, 7, 5, 3, 0, 9] int *d_out; // e.g., [-] ... // Determine temporary device storage requirements void *d_temp_storage = nullptr; size_t temp_storage_bytes = 0; cub::DeviceReduce::Min( d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_out, num_items); // Allocate temporary storage cudaMalloc(&d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes); // Run min-reduction cub::DeviceReduce::Min( d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_out, num_items); // d_out <-- [0]
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (may be a simple pointer type)
OutputIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording the reduced aggregate (may be a simple pointer type)
NumItemsT – [inferred] Type of num_items
- Parameters:
d_temp_storage – [in] Device-accessible allocation of temporary storage. When
nullptr, the required allocation size is written totemp_storage_bytesand no work is done.temp_storage_bytes – [inout] Reference to size in bytes of
d_temp_storageallocationd_in – [in] Pointer to the input sequence of data items
d_out – [out] Pointer to the output aggregate
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)stream – [in]
[optional] CUDA stream to launch kernels within. Default is stream0.
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename OutputIteratorT, typename NumItemsT, typename EnvT = ::cuda::std::execution::env<>>
static inline cudaError_t Min( - InputIteratorT d_in,
- OutputIteratorT d_out,
- NumItemsT num_items,
- EnvT env = {}
Computes a device-wide minimum using the less-than (
<) operator. The result is written to the output iterator.Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
Uses
cuda::std::numeric_limits<T>::max()as the initial value of the reduction.Provides determinism based on the environment’s determinism requirements. To request “run-to-run” determinism, pass
cuda::execution::require(cuda::execution::determinism::run_to_run)as the env parameter.The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_out.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates the min-reduction of a device vector of
intdata elements.auto input = thrust::device_vector<float>{0.0f, 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f}; auto output = thrust::device_vector<float>(1); auto env = cuda::execution::require(cuda::execution::determinism::not_guaranteed); auto error = cub::DeviceReduce::Min(input.begin(), output.begin(), input.size(), env); if (error != cudaSuccess) { std::cerr << "cub::DeviceReduce::Min failed with status: " << error << std::endl; } thrust::device_vector<float> expected{0.0f};
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (may be a simple pointer type)
OutputIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording the reduced aggregate (may be a simple pointer type)
NumItemsT – [inferred] Type of num_items
EnvT – [inferred] Execution environment type. Default is
cuda::std::execution::env<>.
- Parameters:
d_in – [in] Pointer to the input sequence of data items
d_out – [out] Pointer to the output aggregate
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)env – [in]
[optional] Execution environment. Default is cuda::std::execution::env{}.
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename ExtremumOutIteratorT, typename IndexOutIteratorT>
static inline cudaError_t ArgMin( - void *d_temp_storage,
- size_t &temp_storage_bytes,
- InputIteratorT d_in,
- ExtremumOutIteratorT d_min_out,
- IndexOutIteratorT d_index_out,
- ::cuda::std::int64_t num_items,
- cudaStream_t stream = 0
Finds the first device-wide minimum using the less-than (
<) operator and also returns the index of that item.Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
The minimum is written to
d_min_outThe offset of the returned item is written to
d_index_out, the offset type being written is of typecuda::std::int64_t.For zero-length inputs,
cuda::std::numeric_limits<T>::max()}is written tod_min_outand the index1is written tod_index_out.Does not support
<operators that are non-commutative.Provides “run-to-run” determinism for pseudo-associative reduction (e.g., addition of floating point types) on the same GPU device. However, results for pseudo-associative reduction may be inconsistent from one device to a another device of a different compute-capability because CUB can employ different tile-sizing for different architectures.
The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_min_outnord_index_out.When
d_temp_storageisnullptr, no work is done and the required allocation size is returned intemp_storage_bytes. See Determining Temporary Storage Requirements for usage guidance.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates the argmin-reduction of a device vector of
intdata elements.#include <cub/cub.cuh> // or equivalently <cub/device/device_reduce.cuh> #include <cuda/std/cstdint> // Declare, allocate, and initialize device-accessible pointers // for input and output int num_items; // e.g., 7 int *d_in; // e.g., [8, 6, 7, 5, 3, 0, 9] int *d_min_out; // memory for the minimum value cuda::std::int64_t *d_index_out; // memory for the index of the returned value ... // Determine temporary device storage requirements void *d_temp_storage = nullptr; size_t temp_storage_bytes = 0; cub::DeviceReduce::ArgMin(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_min_out, d_index_out, num_items); // Allocate temporary storage cudaMalloc(&d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes); // Run argmin-reduction cub::DeviceReduce::ArgMin(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_min_out, d_index_out, num_items); // d_min_out <-- 0 // d_index_out <-- 5
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (of some type
T) (may be a simple pointer type)ExtremumOutIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording minimum value
IndexOutIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording index of the returned value
- Parameters:
d_temp_storage – [in] Device-accessible allocation of temporary storage. When
nullptr, the required allocation size is written totemp_storage_bytesand no work is done.temp_storage_bytes – [inout] Reference to size in bytes of
d_temp_storageallocationd_in – [in] Iterator to the input sequence of data items
d_min_out – [out] Iterator to which the minimum value is written
d_index_out – [out] Iterator to which the index of the returned value is written
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)stream – [in]
[optional] CUDA stream to launch kernels within. Default is stream0.
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename ExtremumOutIteratorT, typename IndexOutIteratorT, typename EnvT = ::cuda::std::execution::env<>>
static inline cudaError_t ArgMin( - InputIteratorT d_in,
- ExtremumOutIteratorT d_min_out,
- IndexOutIteratorT d_index_out,
- ::cuda::std::int64_t num_items,
- EnvT env = {}
Finds the first device-wide minimum using the less-than (
<) operator and also returns the index of that item.Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
The minimum is written to
d_min_outThe offset of the returned item is written to
d_index_out, the offset type being written is of typecuda::std::int64_t.For zero-length inputs,
cuda::std::numeric_limits<T>::max()}is written tod_min_outand the index1is written tod_index_out.Does not support
<operators that are non-commutative.Provides determinism based on the environment’s determinism requirements. To request “run-to-run” determinism, pass
cuda::execution::require(cuda::execution::determinism::run_to_run)as the env parameter.The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_min_outnord_index_out.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates the argmin-reduction of a device vector of
intdata elements.auto input = thrust::device_vector<float>{3.0f, 1.0f, 4.0f, 0.0f, 2.0f}; auto min_output = thrust::device_vector<float>(1); auto index_output = thrust::device_vector<cuda::std::int64_t>(1); auto env = cuda::execution::require(cuda::execution::determinism::run_to_run); auto error = cub::DeviceReduce::ArgMin(input.begin(), min_output.begin(), index_output.begin(), input.size(), env); if (error != cudaSuccess) { std::cerr << "cub::DeviceReduce::ArgMin failed with status: " << error << std::endl; } thrust::device_vector<float> expected_min{0.0f}; thrust::device_vector<cuda::std::int64_t> expected_index{3};
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (of some type
T) (may be a simple pointer type)ExtremumOutIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording minimum value
IndexOutIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording index of the returned value
EnvT – [inferred] Execution environment type. Default is
cuda::std::execution::env<>.
- Parameters:
d_in – [in] Iterator to the input sequence of data items
d_min_out – [out] Iterator to which the minimum value is written
d_index_out – [out] Iterator to which the index of the returned value is written
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)env – [in]
[optional] Execution environment. Default is
cuda::std::execution::env{}.
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename OutputIteratorT>
static inline cudaError_t ArgMin( - void *d_temp_storage,
- size_t &temp_storage_bytes,
- InputIteratorT d_in,
- OutputIteratorT d_out,
- int num_items,
- cudaStream_t stream = 0
Finds the first device-wide minimum using the less-than (
<) operator, also returning the index of that item.Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
The output value type of
d_outiscub::KeyValuePair<int, T>(assuming the value type ofd_inisT)The minimum is written to
d_out.valueand its offset in the input array is written tod_out.key.The
{1, cuda::std::numeric_limits<T>::max()}tuple is produced for zero-length inputs
Does not support
<operators that are non-commutative.Provides “run-to-run” determinism for pseudo-associative reduction (e.g., addition of floating point types) on the same GPU device. However, results for pseudo-associative reduction may be inconsistent from one device to a another device of a different compute-capability because CUB can employ different tile-sizing for different architectures.
The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_out.When
d_temp_storageisnullptr, no work is done and the required allocation size is returned intemp_storage_bytes. See Determining Temporary Storage Requirements for usage guidance.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates the argmin-reduction of a device vector of
intdata elements.#include <cub/cub.cuh> // or equivalently <cub/device/device_reduce.cuh> // Declare, allocate, and initialize device-accessible pointers // for input and output int num_items; // e.g., 7 int *d_in; // e.g., [8, 6, 7, 5, 3, 0, 9] KeyValuePair<int, int> *d_argmin; // e.g., [{-,-}] ... // Determine temporary device storage requirements void *d_temp_storage = nullptr; size_t temp_storage_bytes = 0; cub::DeviceReduce::ArgMin(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_argmin, num_items); // Allocate temporary storage cudaMalloc(&d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes); // Run argmin-reduction cub::DeviceReduce::ArgMin(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_argmin, num_items); // d_argmin <-- [{5, 0}]
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (of some type
T) (may be a simple pointer type)OutputIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording the reduced aggregate (having value type
cub::KeyValuePair<int, T>) (may be a simple pointer type)
- Parameters:
d_temp_storage – [in] Device-accessible allocation of temporary storage. When
nullptr, the required allocation size is written totemp_storage_bytesand no work is done.temp_storage_bytes – [inout] Reference to size in bytes of
d_temp_storageallocationd_in – [in] Pointer to the input sequence of data items
d_out – [out] Pointer to the output aggregate
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)stream – [in]
[optional] CUDA stream to launch kernels within. Default is stream0.
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename OutputIteratorT, typename NumItemsT>
static inline cudaError_t Max( - void *d_temp_storage,
- size_t &temp_storage_bytes,
- InputIteratorT d_in,
- OutputIteratorT d_out,
- NumItemsT num_items,
- cudaStream_t stream = 0
Computes a device-wide maximum using the greater-than (
>) operator.Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
Uses
cuda::std::numeric_limits<T>::lowest()as the initial value of the reduction.Does not support
>operators that are non-commutative.Provides “run-to-run” determinism for pseudo-associative reduction (e.g., addition of floating point types) on the same GPU device. However, results for pseudo-associative reduction may be inconsistent from one device to a another device of a different compute-capability because CUB can employ different tile-sizing for different architectures.
The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_out.When
d_temp_storageisnullptr, no work is done and the required allocation size is returned intemp_storage_bytes. See Determining Temporary Storage Requirements for usage guidance.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates the max-reduction of a device vector of
intdata elements.#include <cub/cub.cuh> // or equivalently <cub/device/device_reduce.cuh> // Declare, allocate, and initialize device-accessible pointers // for input and output int num_items; // e.g., 7 int *d_in; // e.g., [8, 6, 7, 5, 3, 0, 9] int *d_max; // e.g., [-] ... // Determine temporary device storage requirements void *d_temp_storage = nullptr; size_t temp_storage_bytes = 0; cub::DeviceReduce::Max(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_max, num_items); // Allocate temporary storage cudaMalloc(&d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes); // Run max-reduction cub::DeviceReduce::Max(d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_max, num_items); // d_max <-- [9]
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (may be a simple pointer type)
OutputIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording the reduced aggregate (may be a simple pointer type)
NumItemsT – [inferred] Type of num_items
- Parameters:
d_temp_storage – [in] Device-accessible allocation of temporary storage. When
nullptr, the required allocation size is written totemp_storage_bytesand no work is done.temp_storage_bytes – [inout] Reference to size in bytes of
d_temp_storageallocationd_in – [in] Pointer to the input sequence of data items
d_out – [out] Pointer to the output aggregate
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)stream – [in]
[optional] CUDA stream to launch kernels within. Default is stream0.
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename OutputIteratorT, typename NumItemsT, typename EnvT = ::cuda::std::execution::env<>>
static inline cudaError_t Max( - InputIteratorT d_in,
- OutputIteratorT d_out,
- NumItemsT num_items,
- EnvT env = {}
Computes a device-wide maximum using the greater-than (
>) operator. The result is written to the output iterator.Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
Uses
cuda::std::numeric_limits<T>::lowest()as the initial value of the reduction.Provides determinism based on the environment’s determinism requirements. To request “run-to-run” determinism, pass
cuda::execution::require(cuda::execution::determinism::run_to_run)as the env parameter.The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_out.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates the max-reduction of a device vector of
intdata elements.auto input = thrust::device_vector<float>{0.0f, 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f}; auto output = thrust::device_vector<float>(1); auto env = cuda::execution::require(cuda::execution::determinism::run_to_run); auto error = cub::DeviceReduce::Max(input.begin(), output.begin(), input.size(), env); if (error != cudaSuccess) { std::cerr << "cub::DeviceReduce::Max failed with status: " << error << std::endl; } thrust::device_vector<float> expected{3.0f};
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (may be a simple pointer type)
OutputIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording the reduced aggregate (may be a simple pointer type)
NumItemsT – [inferred] Type of num_items
EnvT – [inferred] Execution environment type. Default is
cuda::std::execution::env<>.
- Parameters:
d_in – [in] Pointer to the input sequence of data items
d_out – [out] Pointer to the output aggregate
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)env – [in]
[optional] Execution environment. Default is
cuda::std::execution::env{}.
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename ExtremumOutIteratorT, typename IndexOutIteratorT>
static inline cudaError_t ArgMax( - void *d_temp_storage,
- size_t &temp_storage_bytes,
- InputIteratorT d_in,
- ExtremumOutIteratorT d_max_out,
- IndexOutIteratorT d_index_out,
- ::cuda::std::int64_t num_items,
- cudaStream_t stream = 0
Finds the first device-wide maximum using the greater-than (
>) operator and also returns the index of that item.Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
The maximum is written to
d_max_outThe offset of the returned item is written to
d_index_out, the offset type being written is of typecuda::std::int64_t.For zero-length inputs,
cuda::std::numeric_limits<T>::max()}is written tod_max_outand the index1is written tod_index_out.Does not support
>operators that are non-commutative.Provides “run-to-run” determinism for pseudo-associative reduction (e.g., addition of floating point types) on the same GPU device. However, results for pseudo-associative reduction may be inconsistent from one device to a another device of a different compute-capability because CUB can employ different tile-sizing for different architectures.
The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_out.When
d_temp_storageisnullptr, no work is done and the required allocation size is returned intemp_storage_bytes. See Determining Temporary Storage Requirements for usage guidance.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates the argmax-reduction of a device vector of int data elements.
#include <cub/cub.cuh> // or equivalently <cub/device/device_reduce.cuh> #include <cuda/std/cstdint> // Declare, allocate, and initialize device-accessible pointers // for input and output int num_items; // e.g., 7 int *d_in; // e.g., [8, 6, 7, 5, 3, 0, 9] int *d_max_out; // memory for the maximum value cuda::std::int64_t *d_index_out; // memory for the index of the returned value ... // Determine temporary device storage requirements void *d_temp_storage = nullptr; size_t temp_storage_bytes = 0; cub::DeviceReduce::ArgMax( d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_max_out, d_index_out, num_items); // Allocate temporary storage cudaMalloc(&d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes); // Run argmax-reduction cub::DeviceReduce::ArgMax( d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_max_out, d_index_out, num_items); // d_max_out <-- 9 // d_index_out <-- 6
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (of some type
T) (may be a simple pointer type)ExtremumOutIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording maximum value
IndexOutIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording index of the returned value
- Parameters:
d_temp_storage – [in] Device-accessible allocation of temporary storage. When
nullptr, the required allocation size is written totemp_storage_bytesand no work is done.temp_storage_bytes – [inout] Reference to size in bytes of
d_temp_storageallocationd_in – [in] Pointer to the input sequence of data items
d_max_out – [out] Iterator to which the maximum value is written
d_index_out – [out] Iterator to which the index of the returned value is written
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)stream – [in]
[optional] CUDA stream to launch kernels within. Default is stream0.
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename OutputIteratorT>
static inline cudaError_t ArgMax( - void *d_temp_storage,
- size_t &temp_storage_bytes,
- InputIteratorT d_in,
- OutputIteratorT d_out,
- int num_items,
- cudaStream_t stream = 0
Finds the first device-wide maximum using the greater-than (
>) operator, also returning the index of that itemAdded in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
The output value type of
d_outiscub::KeyValuePair<int, T>(assuming the value type ofd_inisT)The maximum is written to
d_out.valueand its offset in the input array is written tod_out.key.The
{1, cuda::std::numeric_limits<T>::lowest()}tuple is produced for zero-length inputs
Does not support
>operators that are non-commutative.Provides “run-to-run” determinism for pseudo-associative reduction (e.g., addition of floating point types) on the same GPU device. However, results for pseudo-associative reduction may be inconsistent from one device to a another device of a different compute-capability because CUB can employ different tile-sizing for different architectures.
The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_out.When
d_temp_storageisnullptr, no work is done and the required allocation size is returned intemp_storage_bytes. See Determining Temporary Storage Requirements for usage guidance.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates the argmax-reduction of a device vector of int data elements.
#include <cub/cub.cuh> // or equivalently <cub/device/device_reduce.cuh> // Declare, allocate, and initialize device-accessible pointers // for input and output int num_items; // e.g., 7 int *d_in; // e.g., [8, 6, 7, 5, 3, 0, 9] KeyValuePair<int, int> *d_argmax; // e.g., [{-,-}] ... // Determine temporary device storage requirements void *d_temp_storage = nullptr; size_t temp_storage_bytes = 0; cub::DeviceReduce::ArgMax( d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_argmax, num_items); // Allocate temporary storage cudaMalloc(&d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes); // Run argmax-reduction cub::DeviceReduce::ArgMax( d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_in, d_argmax, num_items); // d_argmax <-- [{6, 9}]
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (of some type
T) (may be a simple pointer type)OutputIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording the reduced aggregate (having value type
cub::KeyValuePair<int, T>) (may be a simple pointer type)
- Parameters:
d_temp_storage – [in] Device-accessible allocation of temporary storage. When
nullptr, the required allocation size is written totemp_storage_bytesand no work is done.temp_storage_bytes – [inout] Reference to size in bytes of
d_temp_storageallocationd_in – [in] Pointer to the input sequence of data items
d_out – [out] Pointer to the output aggregate
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)stream – [in]
[optional] CUDA stream to launch kernels within. Default is stream0.
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename ExtremumOutIteratorT, typename IndexOutIteratorT, typename EnvT = ::cuda::std::execution::env<>>
static inline cudaError_t ArgMax( - InputIteratorT d_in,
- ExtremumOutIteratorT d_max_out,
- IndexOutIteratorT d_index_out,
- ::cuda::std::int64_t num_items,
- EnvT env = {}
Finds the first device-wide maximum using the greater-than (
>) operator and also returns the index of that item.Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
The maximum is written to
d_max_outThe offset of the returned item is written to
d_index_out, the offset type being written is of typecuda::std::int64_t.For zero-length inputs,
cuda::std::numeric_limits<T>::lowest()}is written tod_max_outand the index1is written tod_index_out.Does not support
>operators that are non-commutative.Provides determinism based on the environment’s determinism requirements. To request “run-to-run” determinism, pass
cuda::execution::require(cuda::execution::determinism::run_to_run)as the env parameter.The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_max_outnord_index_out.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates the argmax-reduction of a device vector of
intdata elements.auto input = thrust::device_vector<float>{3.0f, 1.0f, 4.0f, 0.0f, 2.0f}; auto max_output = thrust::device_vector<float>(1); auto index_output = thrust::device_vector<cuda::std::int64_t>(1); auto env = cuda::execution::require(cuda::execution::determinism::not_guaranteed); auto error = cub::DeviceReduce::ArgMax(input.begin(), max_output.begin(), index_output.begin(), input.size(), env); if (error != cudaSuccess) { std::cerr << "cub::DeviceReduce::ArgMax failed with status: " << error << std::endl; } thrust::device_vector<float> expected_max{4.0f}; thrust::device_vector<cuda::std::int64_t> expected_index{2};
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (of some type
T) (may be a simple pointer type)ExtremumOutIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording maximum value
IndexOutIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording index of the returned value
EnvT – [inferred] Execution environment type. Default is
cuda::std::execution::env<>.
- Parameters:
d_in – [in] Iterator to the input sequence of data items
d_max_out – [out] Iterator to which the maximum value is written
d_index_out – [out] Iterator to which the index of the returned value is written
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)env – [in]
[optional] Execution environment. Default is
cuda::std::execution::env{}.
-
template<typename InputIteratorT, typename OutputIteratorT, typename ReductionOpT, typename TransformOpT, typename T, typename NumItemsT>
static inline cudaError_t TransformReduce( - void *d_temp_storage,
- size_t &temp_storage_bytes,
- InputIteratorT d_in,
- OutputIteratorT d_out,
- NumItemsT num_items,
- ReductionOpT reduction_op,
- TransformOpT transform_op,
- T init,
- cudaStream_t stream = 0
Fuses transform and reduce operations
Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
Does not support binary reduction operators that are non-commutative.
Provides “run-to-run” determinism for pseudo-associative reduction (e.g., addition of floating point types) on the same GPU device. However, results for pseudo-associative reduction may be inconsistent from one device to a another device of a different compute-capability because CUB can employ different tile-sizing for different architectures.
The range
[d_in, d_in + num_items)shall not overlapd_out.When
d_temp_storageisnullptr, no work is done and the required allocation size is returned intemp_storage_bytes. See Determining Temporary Storage Requirements for usage guidance.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates a user-defined min-reduction of a device vector of int data elements.
#include <cub/cub.cuh> // or equivalently <cub/device/device_reduce.cuh> thrust::device_vector<int> in = { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; thrust::device_vector<int> out(1); size_t temp_storage_bytes = 0; uint8_t *d_temp_storage = nullptr; const int init = 42; cub::DeviceReduce::TransformReduce( d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, in.begin(), out.begin(), in.size(), cuda::std::plus<>{}, square_t{}, init); thrust::device_vector<uint8_t> temp_storage(temp_storage_bytes); d_temp_storage = temp_storage.data().get(); cub::DeviceReduce::TransformReduce( d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, in.begin(), out.begin(), in.size(), cuda::std::plus<>{}, square_t{}, init); // out[0] <-- 72
- Template Parameters:
InputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input items (may be a simple pointer type)
OutputIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording the reduced aggregate (may be a simple pointer type)
ReductionOpT – [inferred] Binary reduction functor type having member
T operator()(const T &a, const T &b)TransformOpT – [inferred] Unary reduction functor type having member
auto operator()(const T &a)T – [inferred] Data element type that is convertible to the
valuetype ofInputIteratorTNumItemsT – [inferred] Type of num_items
- Parameters:
d_temp_storage – [in] Device-accessible allocation of temporary storage. When
nullptr, the required allocation size is written totemp_storage_bytesand no work is done.temp_storage_bytes – [inout] Reference to size in bytes of
d_temp_storageallocationd_in – [in] Pointer to the input sequence of data items
d_out – [out] Pointer to the output aggregate
num_items – [in] Total number of input items (i.e., length of
d_in)reduction_op – [in] Binary reduction functor
transform_op – [in] Unary transform functor
init – [in] Initial value of the reduction
stream – [in]
[optional] CUDA stream to launch kernels within. Default is stream0.
-
template<typename KeysInputIteratorT, typename UniqueOutputIteratorT, typename ValuesInputIteratorT, typename AggregatesOutputIteratorT, typename NumRunsOutputIteratorT, typename ReductionOpT, typename NumItemsT>
static inline cudaError_t ReduceByKey( - void *d_temp_storage,
- size_t &temp_storage_bytes,
- KeysInputIteratorT d_keys_in,
- UniqueOutputIteratorT d_unique_out,
- ValuesInputIteratorT d_values_in,
- AggregatesOutputIteratorT d_aggregates_out,
- NumRunsOutputIteratorT d_num_runs_out,
- ReductionOpT reduction_op,
- NumItemsT num_items,
- cudaStream_t stream = 0
Reduces segments of values, where segments are demarcated by corresponding runs of identical keys.
Added in version 2.2.0: First appears in CUDA Toolkit 12.3.
This operation computes segmented reductions within
d_values_inusing the specified binaryreduction_opfunctor. The segments are identified by “runs” of corresponding keys in d_keys_in, where runs are maximal ranges of consecutive, identical keys. For the ith run encountered, the last key of the run and the corresponding value aggregate of that run are written tod_unique_out[i]andd_aggregates_out[i], respectively. The total number of runs encountered is written tod_num_runs_out.The
==equality operator is used to determine whether keys are equivalentProvides “run-to-run” determinism for pseudo-associative reduction (e.g., addition of floating point types) on the same GPU device. However, results for pseudo-associative reduction may be inconsistent from one device to a another device of a different compute-capability because CUB can employ different tile-sizing for different architectures.
Let
outbe any of[d_unique_out, d_unique_out + *d_num_runs_out)[d_aggregates_out, d_aggregates_out + *d_num_runs_out)d_num_runs_out. The ranges represented byoutshall not overlap[d_keys_in, d_keys_in + num_items),[d_values_in, d_values_in + num_items)noroutin any way.When
d_temp_storageisnullptr, no work is done and the required allocation size is returned intemp_storage_bytes. See Determining Temporary Storage Requirements for usage guidance.
Snippet#
The code snippet below illustrates the segmented reduction of
intvalues grouped by runs of associatedintkeys.#include <cub/cub.cuh> // or equivalently <cub/device/device_reduce.cuh> // CustomMin functor struct CustomMin { template <typename T> __device__ __forceinline__ T operator()(const T &a, const T &b) const { return (b < a) ? b : a; } }; // Declare, allocate, and initialize device-accessible pointers // for input and output int num_items; // e.g., 8 int *d_keys_in; // e.g., [0, 2, 2, 9, 5, 5, 5, 8] int *d_values_in; // e.g., [0, 7, 1, 6, 2, 5, 3, 4] int *d_unique_out; // e.g., [-, -, -, -, -, -, -, -] int *d_aggregates_out; // e.g., [-, -, -, -, -, -, -, -] int *d_num_runs_out; // e.g., [-] CustomMin reduction_op; ... // Determine temporary device storage requirements void *d_temp_storage = nullptr; size_t temp_storage_bytes = 0; cub::DeviceReduce::ReduceByKey( d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_keys_in, d_unique_out, d_values_in, d_aggregates_out, d_num_runs_out, reduction_op, num_items); // Allocate temporary storage cudaMalloc(&d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes); // Run reduce-by-key cub::DeviceReduce::ReduceByKey( d_temp_storage, temp_storage_bytes, d_keys_in, d_unique_out, d_values_in, d_aggregates_out, d_num_runs_out, reduction_op, num_items); // d_unique_out <-- [0, 2, 9, 5, 8] // d_aggregates_out <-- [0, 1, 6, 2, 4] // d_num_runs_out <-- [5]
- Template Parameters:
KeysInputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input keys (may be a simple pointer type)
UniqueOutputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access output iterator type for writing unique output keys (may be a simple pointer type)
ValuesInputIteratorT – [inferred] Random-access input iterator type for reading input values (may be a simple pointer type)
AggregatesOutputIterator – [inferred] Random-access output iterator type for writing output value aggregates (may be a simple pointer type)
NumRunsOutputIteratorT – [inferred] Output iterator type for recording the number of runs encountered (may be a simple pointer type)
ReductionOpT – [inferred] Binary reduction functor type having member
T operator()(const T &a, const T &b)NumItemsT – [inferred] Type of num_items
- Parameters:
d_temp_storage – [in] Device-accessible allocation of temporary storage. When
nullptr, the required allocation size is written totemp_storage_bytesand no work is done.temp_storage_bytes – [inout] Reference to size in bytes of
d_temp_storageallocationd_keys_in – [in] Pointer to the input sequence of keys
d_unique_out – [out] Pointer to the output sequence of unique keys (one key per run)
d_values_in – [in] Pointer to the input sequence of corresponding values
d_aggregates_out – [out] Pointer to the output sequence of value aggregates (one aggregate per run)
d_num_runs_out – [out] Pointer to total number of runs encountered (i.e., the length of
d_unique_out)reduction_op – [in] Binary reduction functor
num_items – [in] Total number of associated key+value pairs (i.e., the length of
d_in_keysandd_in_values)stream – [in]
[optional] CUDA stream to launch kernels within. Default is stream0.