DFT-D3 Dispersion Benchmarks#
This page presents benchmark results for DFT-D3 dispersion corrections across different GPU hardware. Results show the scaling behavior with increasing system size for periodic systems, including both single-system and batched computations.
Warning
These results are intended to be indicative only: your actual performance may vary depending on the atomic system topology, software and hardware configuration and we encourage users to benchmark on their own systems of interest.
How to Read These Charts#
Time Scaling : Median execution time (ms) vs. system size. Lower is better. Timings exclude neighbor list construction, and only comprises the DFT-D3 computation.
Throughput : Atoms processed per millisecond. Higher is better. This indicates where the scaling point where the GPU saturates.
Memory : Peak GPU memory usage (MB) vs. system size. This is particularly useful for estimating/gauging memory requirements for your system.
Performance Results#
Simple comparison of single (non-batched) system computations between backends, where we scale up the size of the supercell.
Time Scaling
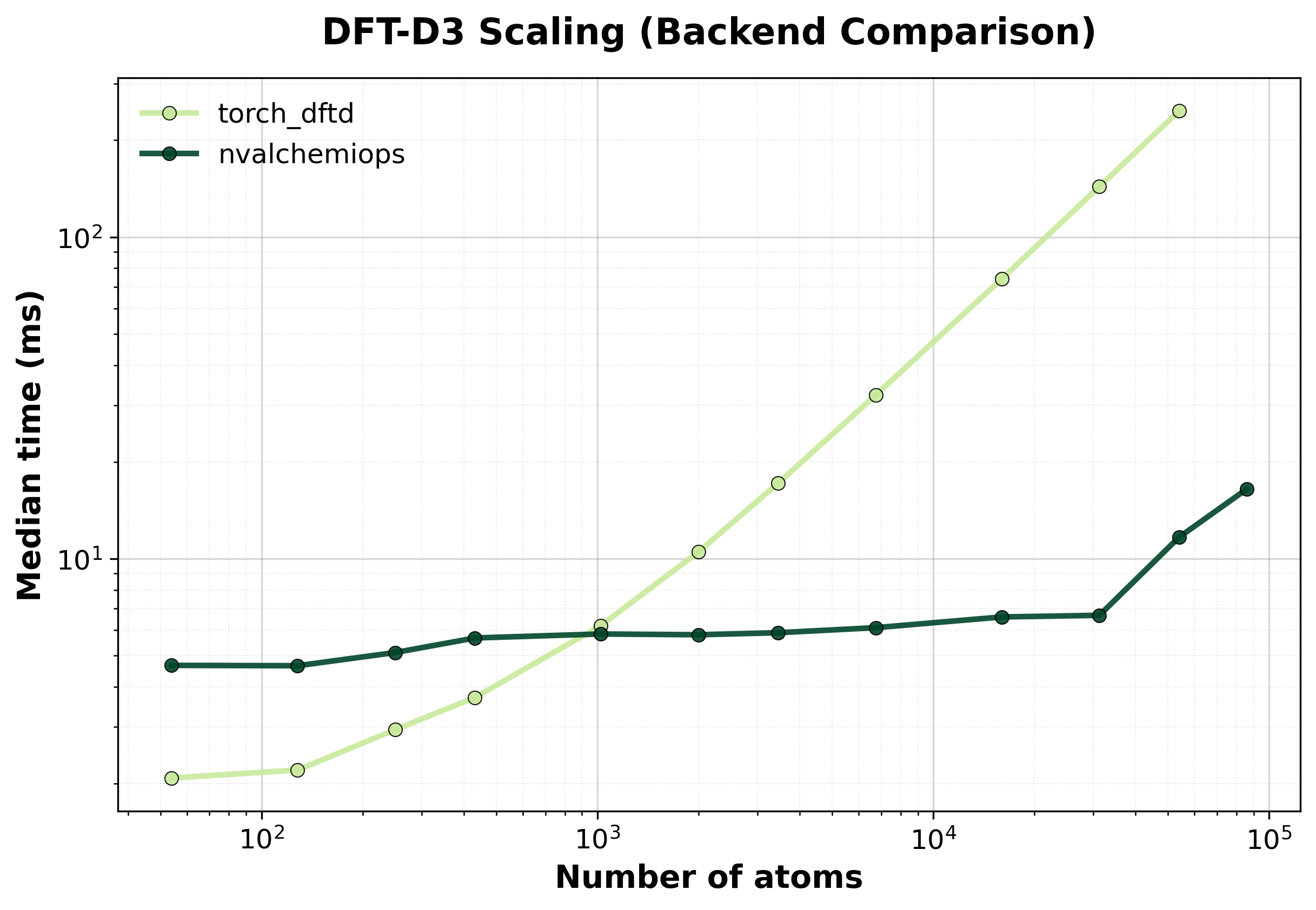
Median execution time comparison between backends for single systems.#
Throughput
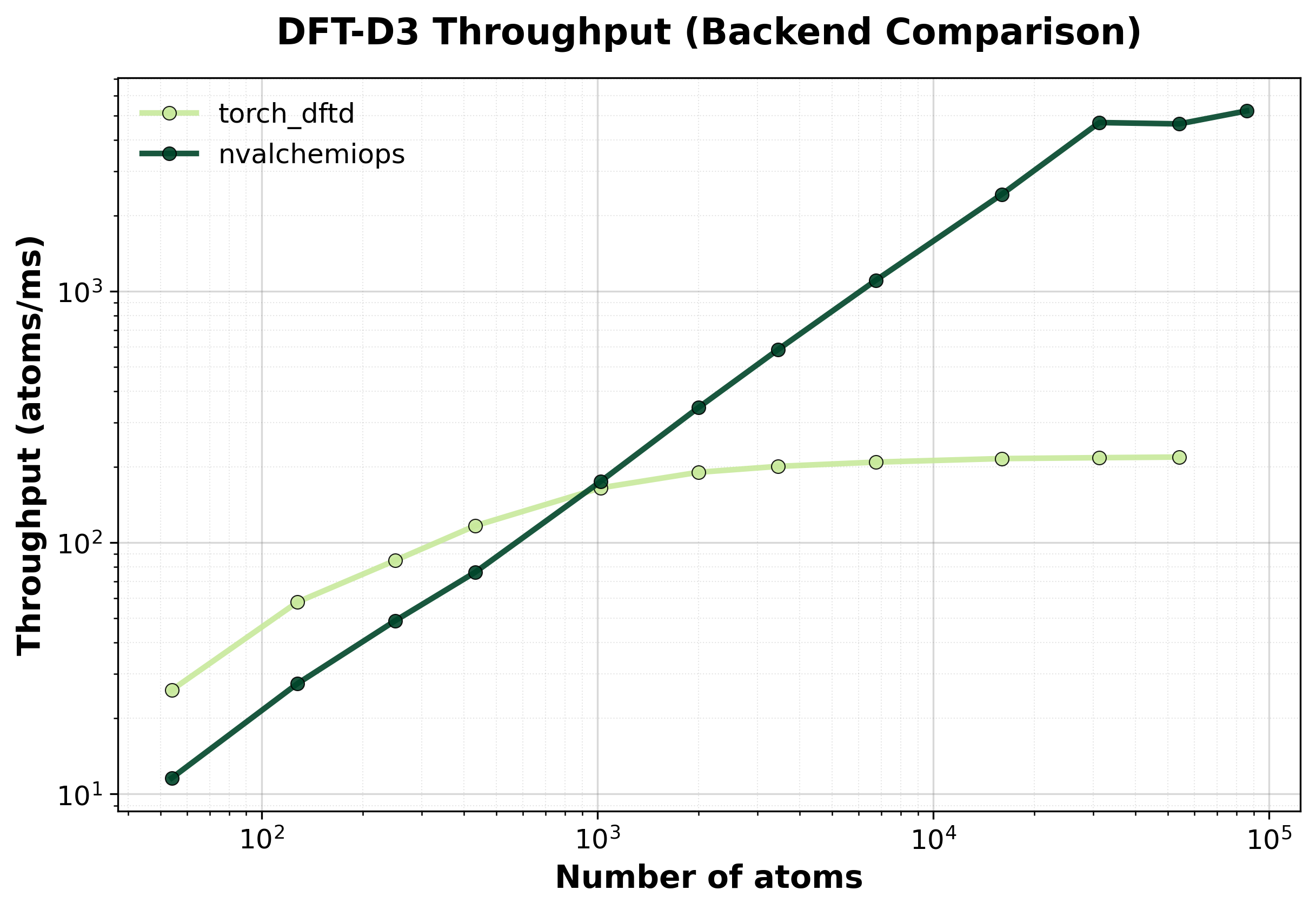
Throughput (atoms/ms) comparison between backends. Higher values indicate better performance.#
Memory Usage
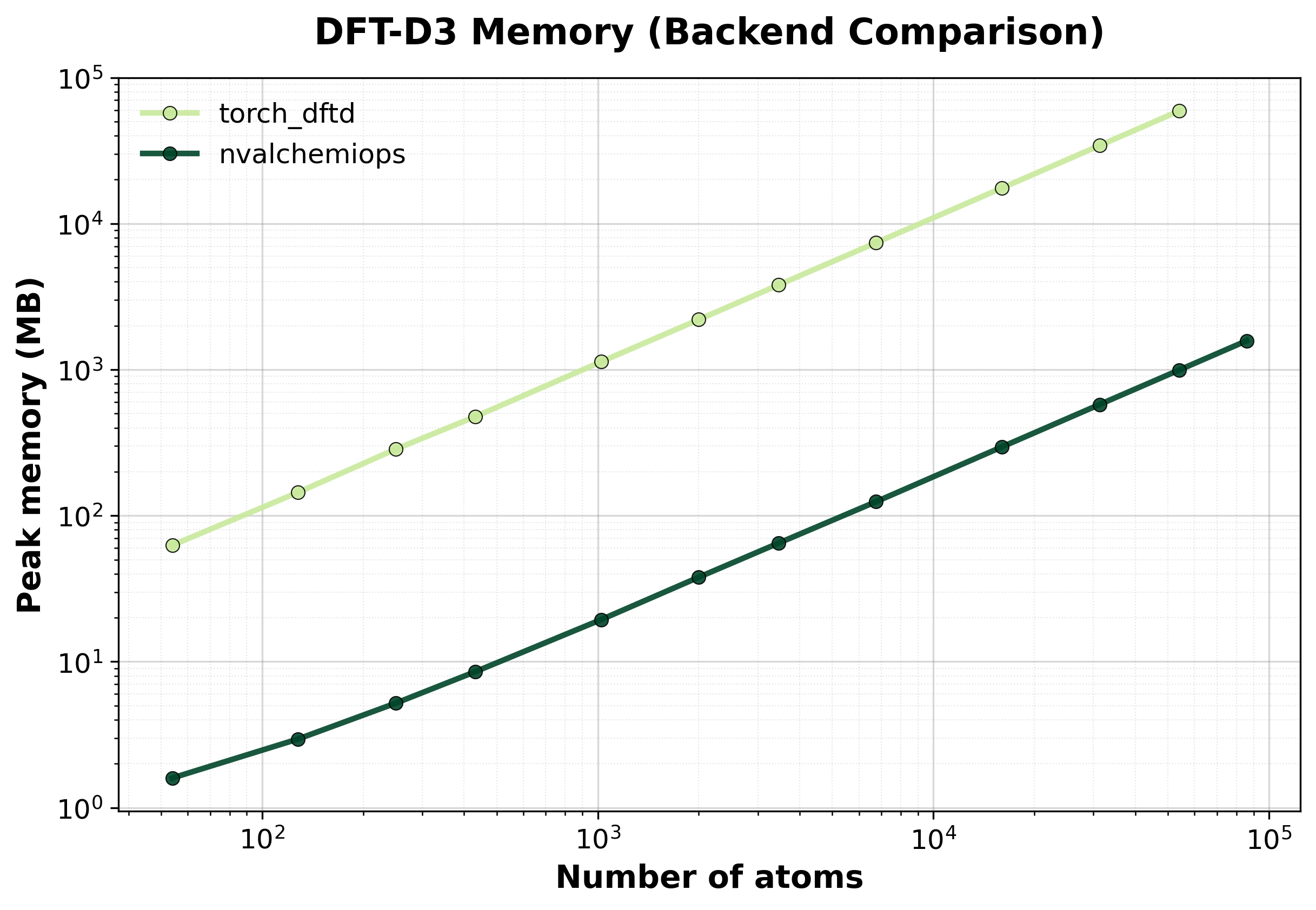
Peak GPU memory consumption comparison between backends. Lower is better, indicating that the backend has lower memory requirements.#
Scaling of single and batched computation with the nvalchemiops backend.
Shows how performance scales with different batch sizes.
Time Scaling
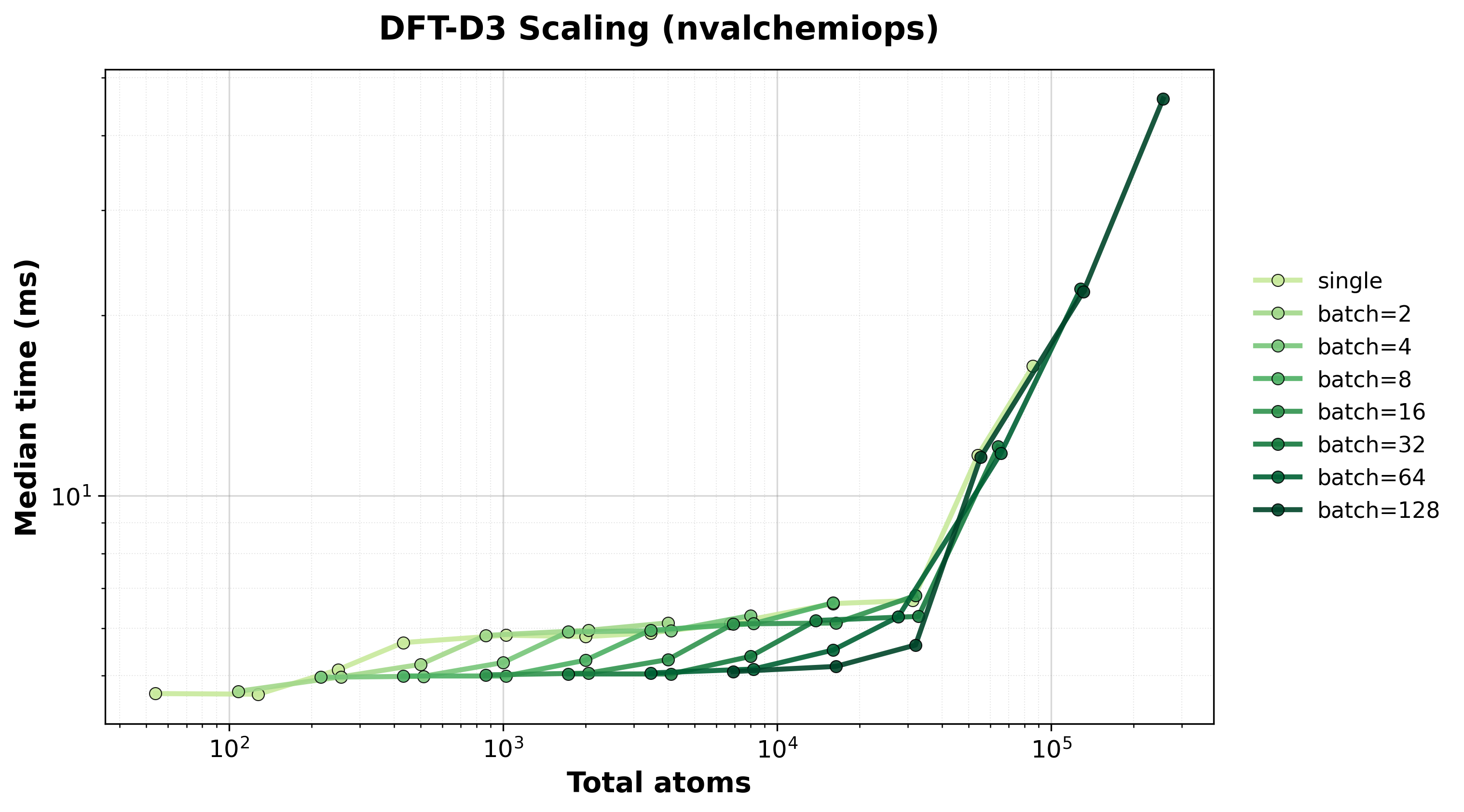
Execution time scaling for single and batched systems.#
Throughput
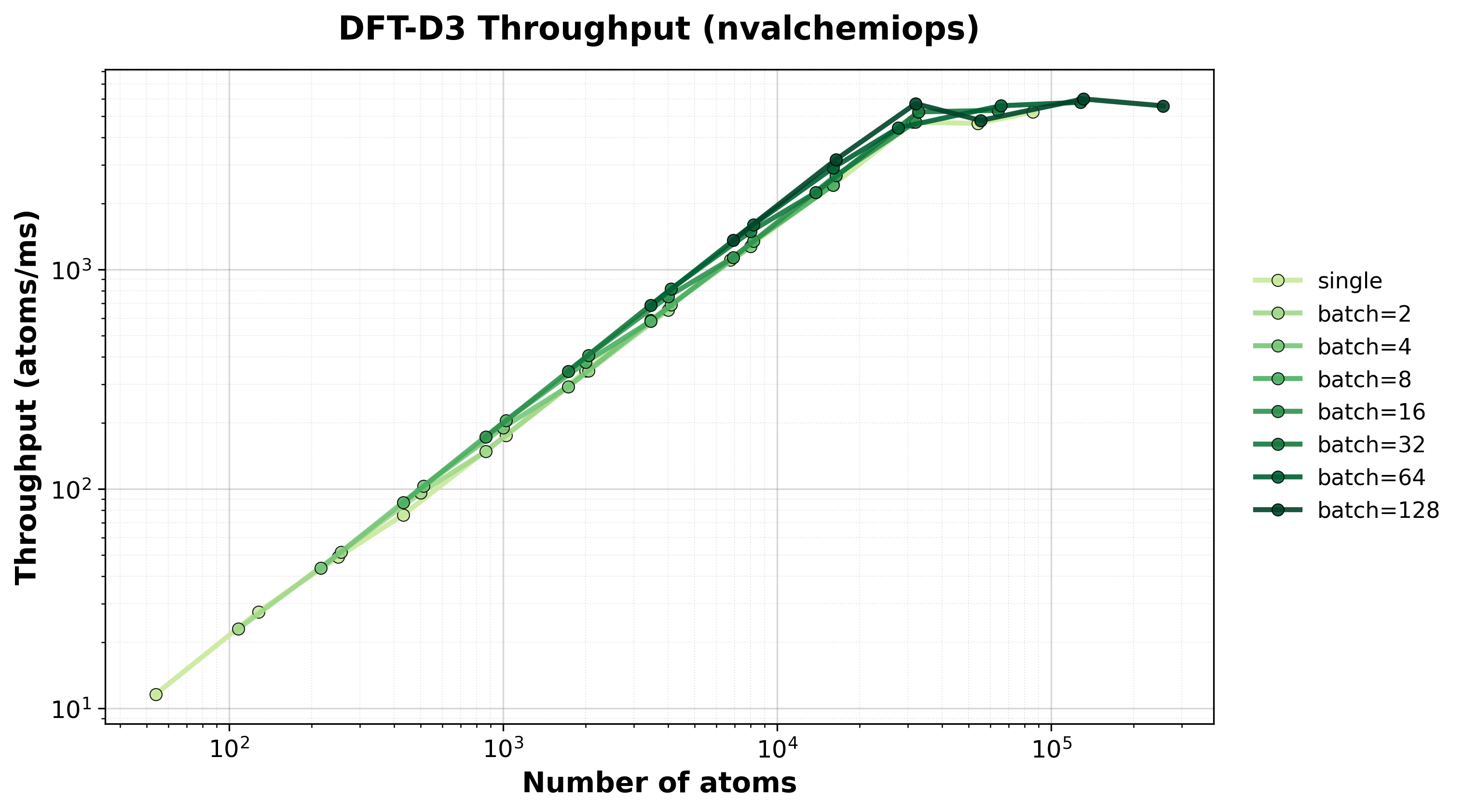
Throughput (atoms/ms) for single and batched systems.#
Memory Usage
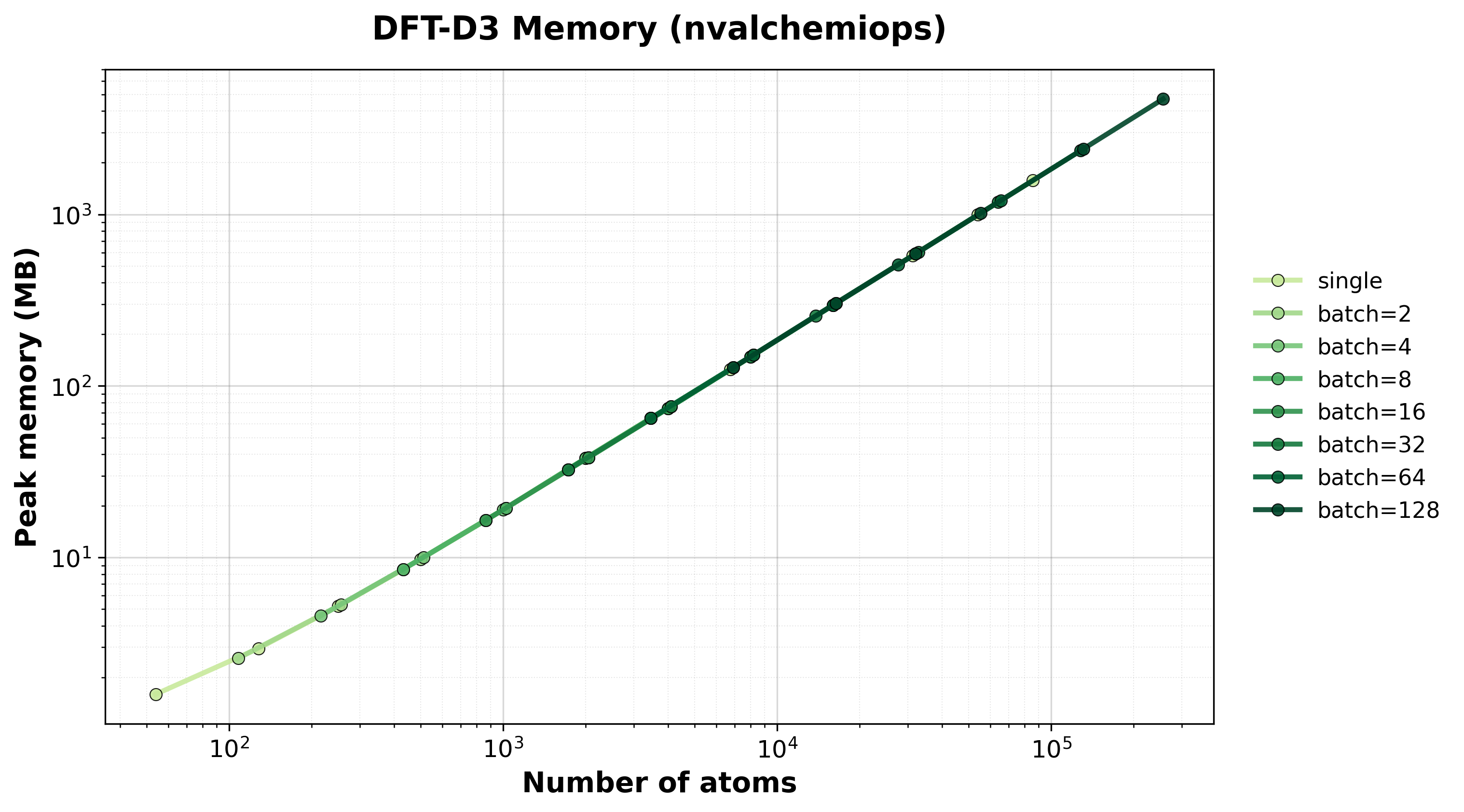
Peak GPU memory consumption for single and batched systems.#
Scaling of single and batched computation with the torch-dftd backend.
Shows how performance scales with different batch sizes.
Time Scaling
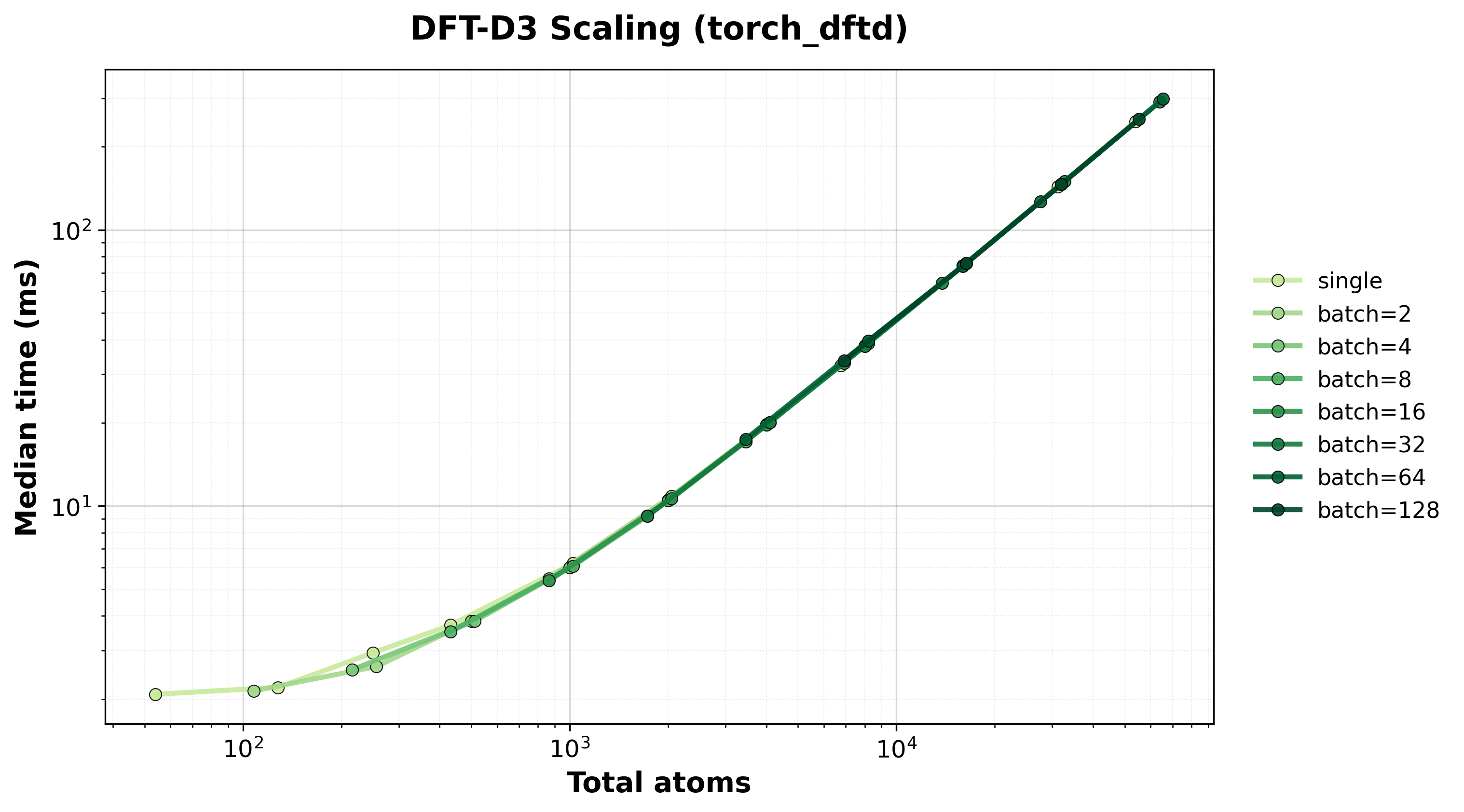
Execution time scaling for single and batched systems.#
Throughput
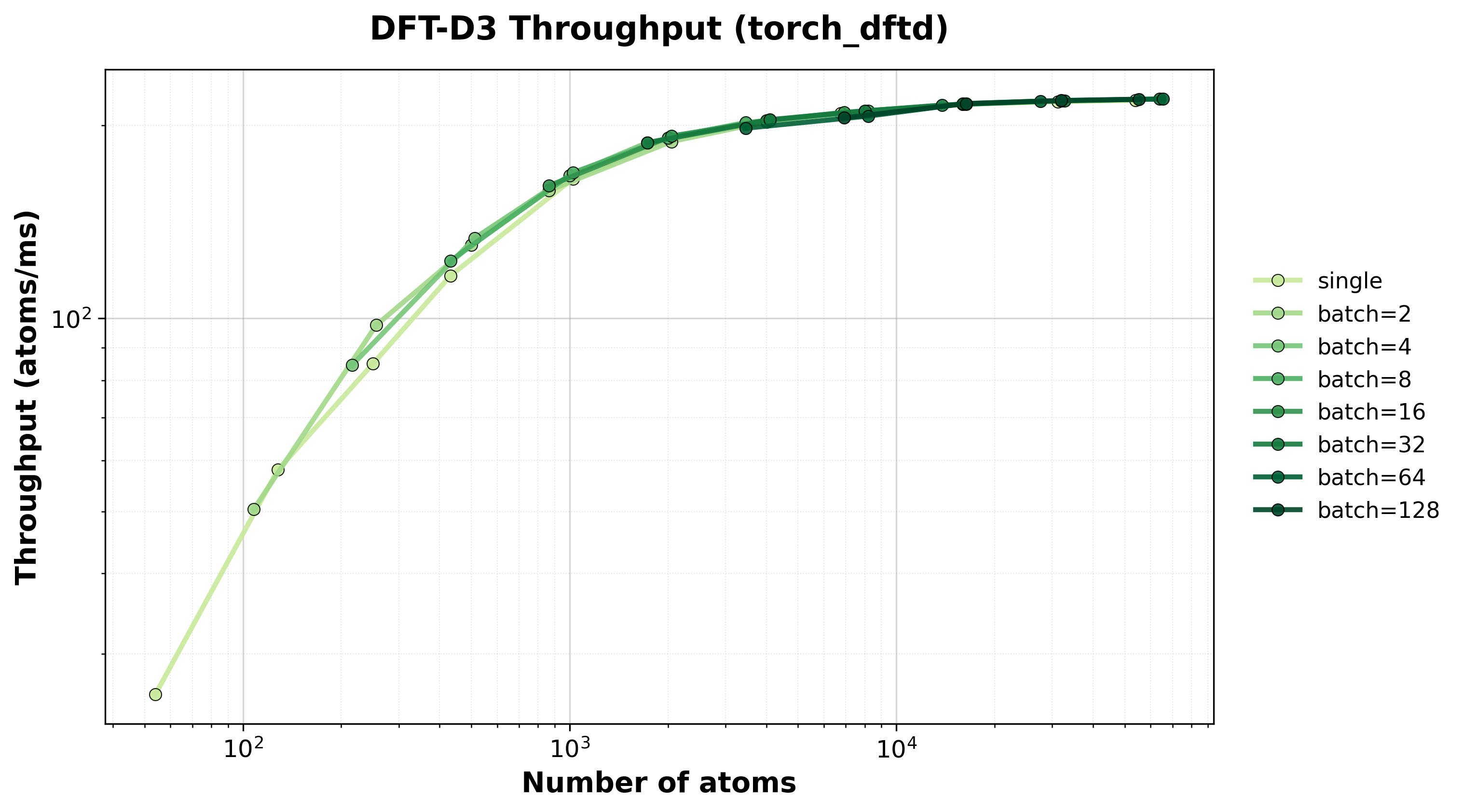
Throughput (atoms/ms) for single and batched systems.#
Memory Usage
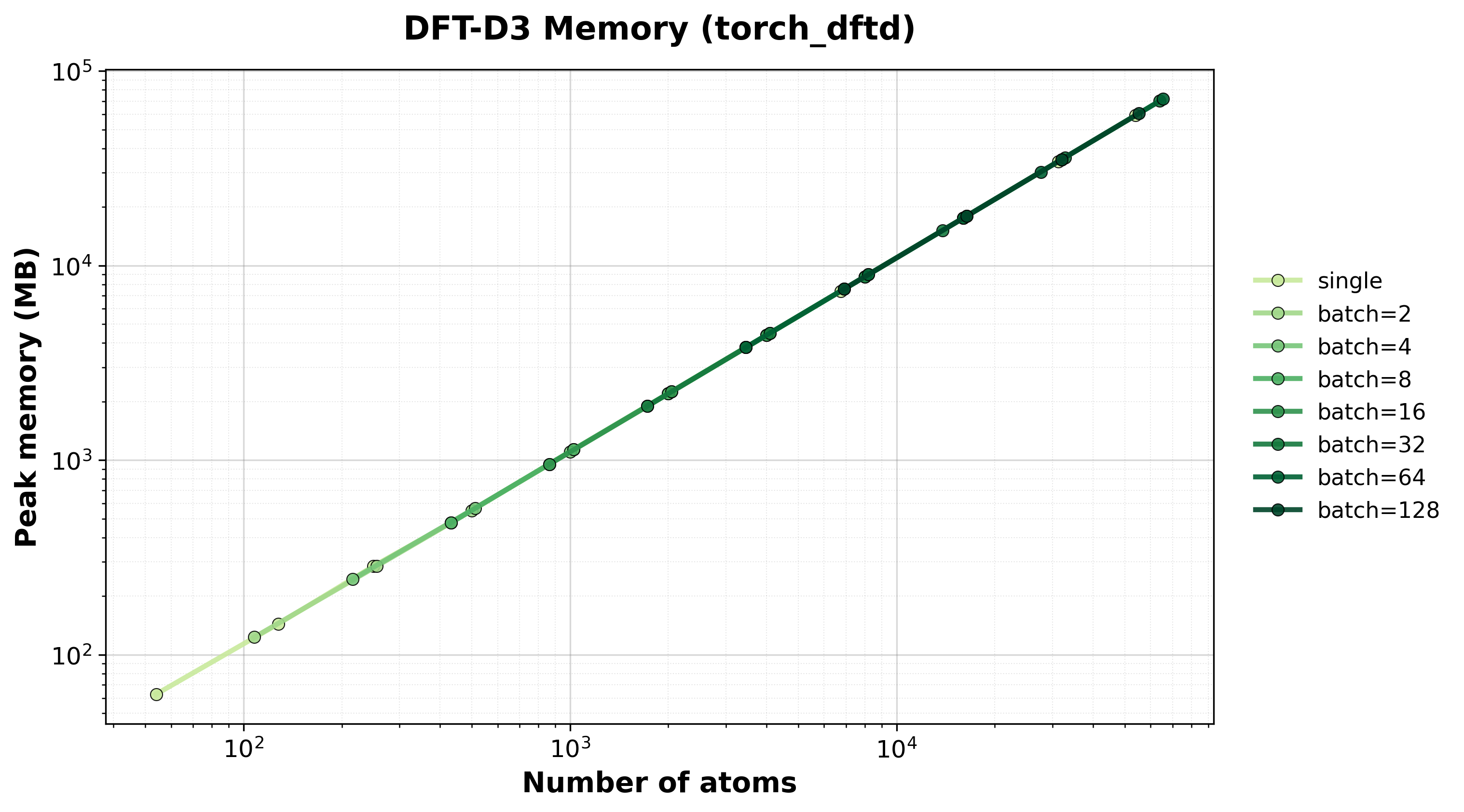
Peak GPU memory consumption for single and batched systems.#
Hardware Information#
GPU: NVIDIA H100 80GB HBM3
Benchmark Configuration#
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
Cutoff |
21.2 Å (40 Bohr) |
System Type |
CsCl supercells with periodic boundaries |
Neighbor List |
Cell list algorithm (\(O(N)\) scaling) |
Warmup Iterations |
3 |
Timing Iterations |
10 |
Precision |
|
DFT-D3 Parameters#
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
Functional |
BJ-damping |
|
0.4289 |
|
4.4407 |
|
1.0 |
|
0.7875 |
Interpreting Results#
total_atoms
: Total number of atoms in the supercell.
batch_size
: Number of systems processed simultaneously.
supercell_size
: Linear dimension of supercell (\(n^3\)).
total_neighbors
: Total number of neighbor pairs within cutoff.
median_time_ms
: Median execution time in milliseconds (lower is better).
peak_memory_mb
: Peak GPU memory usage in megabytes.
Note
Timings exclude neighbor list construction and only measure the DFT-D3 energy/force calculation.
Running Your Own Benchmarks#
To generate benchmark results for your hardware:
nvalchemiops Backend (default)#
cd benchmarks/interactions/dispersion
python benchmark_dftd3.py \
--config benchmark_config.yaml \
--backend warp \
--output-dir ../../../docs/benchmarks/benchmark_results
torch-dftd Backend#
cd benchmarks/interactions/dispersion
python benchmark_dftd3.py \
--config benchmark_config.yaml \
--backend torch_dftd \
--output-dir ../../../docs/benchmarks/benchmark_results
Options#
--backend {warp,torch_dftd}
: Select backend (default: warp).
--gpu-sku <name>
: Override GPU SKU name for output files (default: auto-detect).
--config <path>
: Path to YAML configuration file.
Results will be saved as CSV files and plots will be automatically generated during the next documentation build.
