Neighbor List Benchmarks#
This page presents benchmark results for various neighbor list algorithms
across different GPU hardware. Results are automatically generated from
CSV files in the benchmark_results/ directory.
Warning
These results are intended to be indicative only: your actual performance may vary depending on the atomic system topology, software and hardware configuration and we encourage users to benchmark on their own systems of interest.
How to Read These Charts#
Time Scaling : Median execution time (ms) vs. system size. Lower is better. Cell list algorithms show \(O(N)\) scaling while naive algorithms show \(O(N^2)\).
Throughput : Atoms processed per millisecond. Higher is better. This metric helps compare efficiency across different system sizes.
Memory : Peak GPU memory usage (MB) vs. system size. Useful for estimating memory requirements for your target system.
Performance Results#
Select a method to view detailed benchmark data and scaling plots:
Brute-force \(O(N^2)\) algorithm. Best for very small systems where the overhead of cell list construction exceeds the computational savings.
Time Scaling
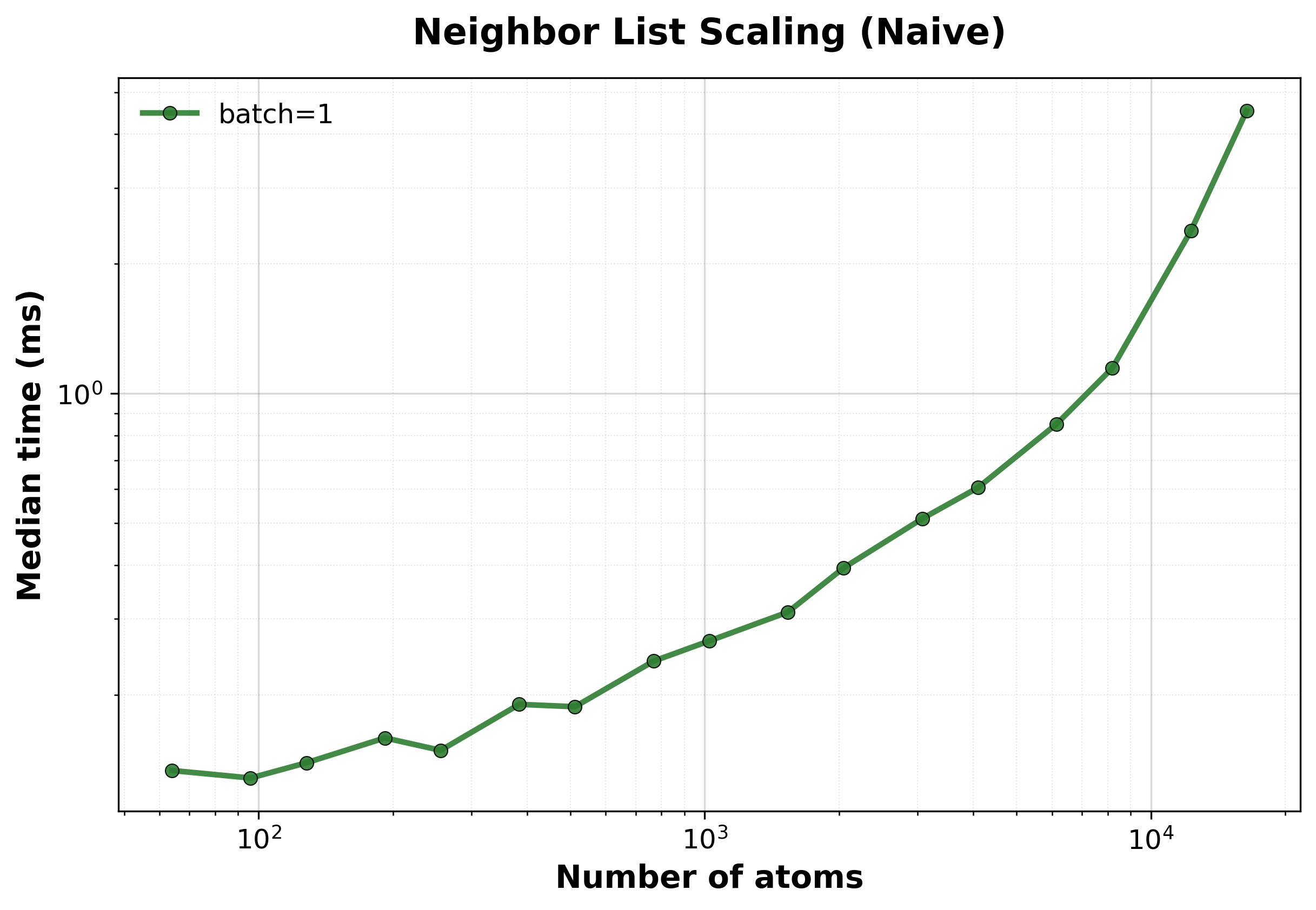
Median execution time vs. system size. The \(O(N^2)\) scaling becomes apparent for larger systems.#
Throughput
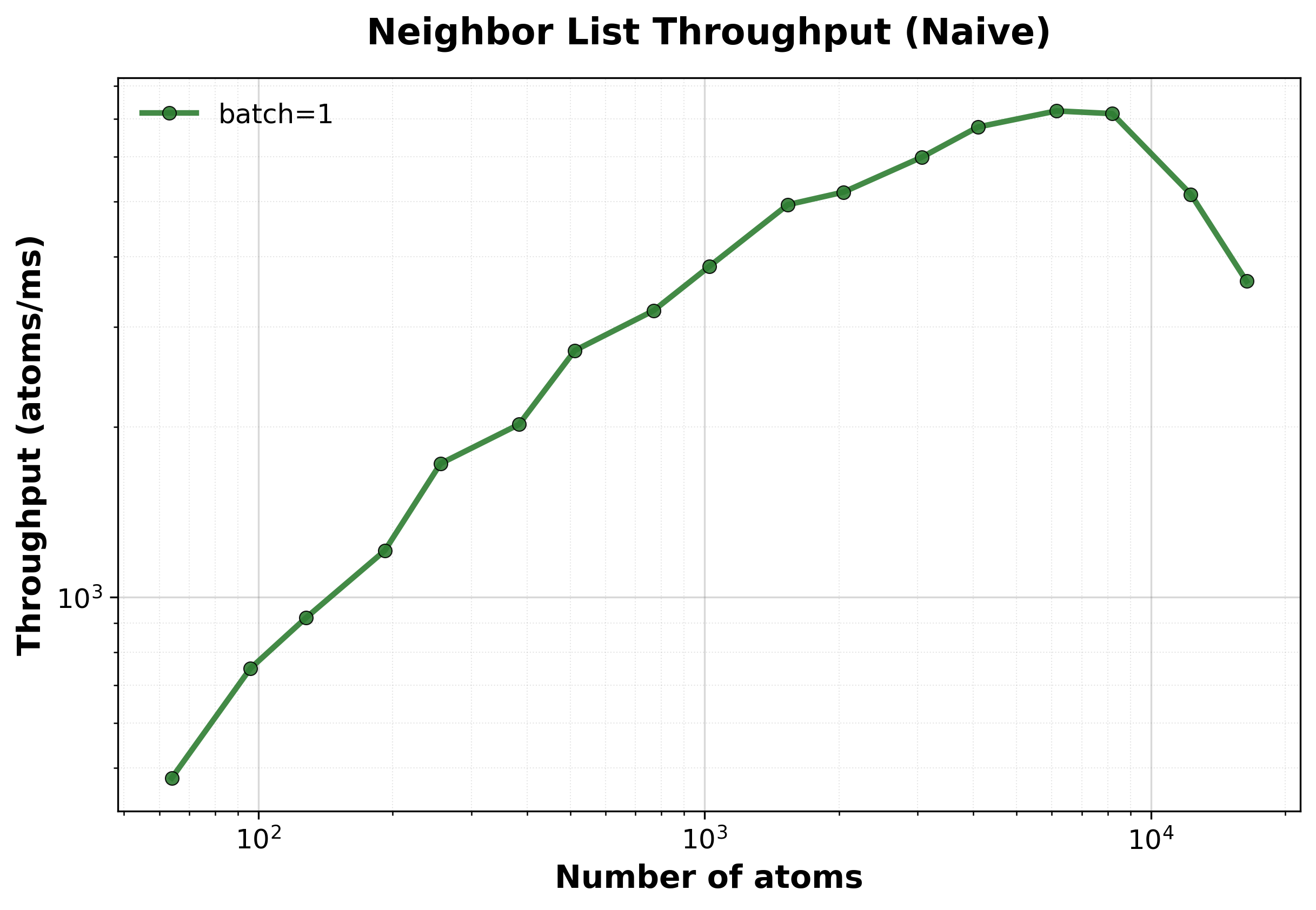
Throughput (atoms/ms) vs. system size. Throughput decreases as system size grows due to \(O(N^2)\) scaling.#
Memory Usage
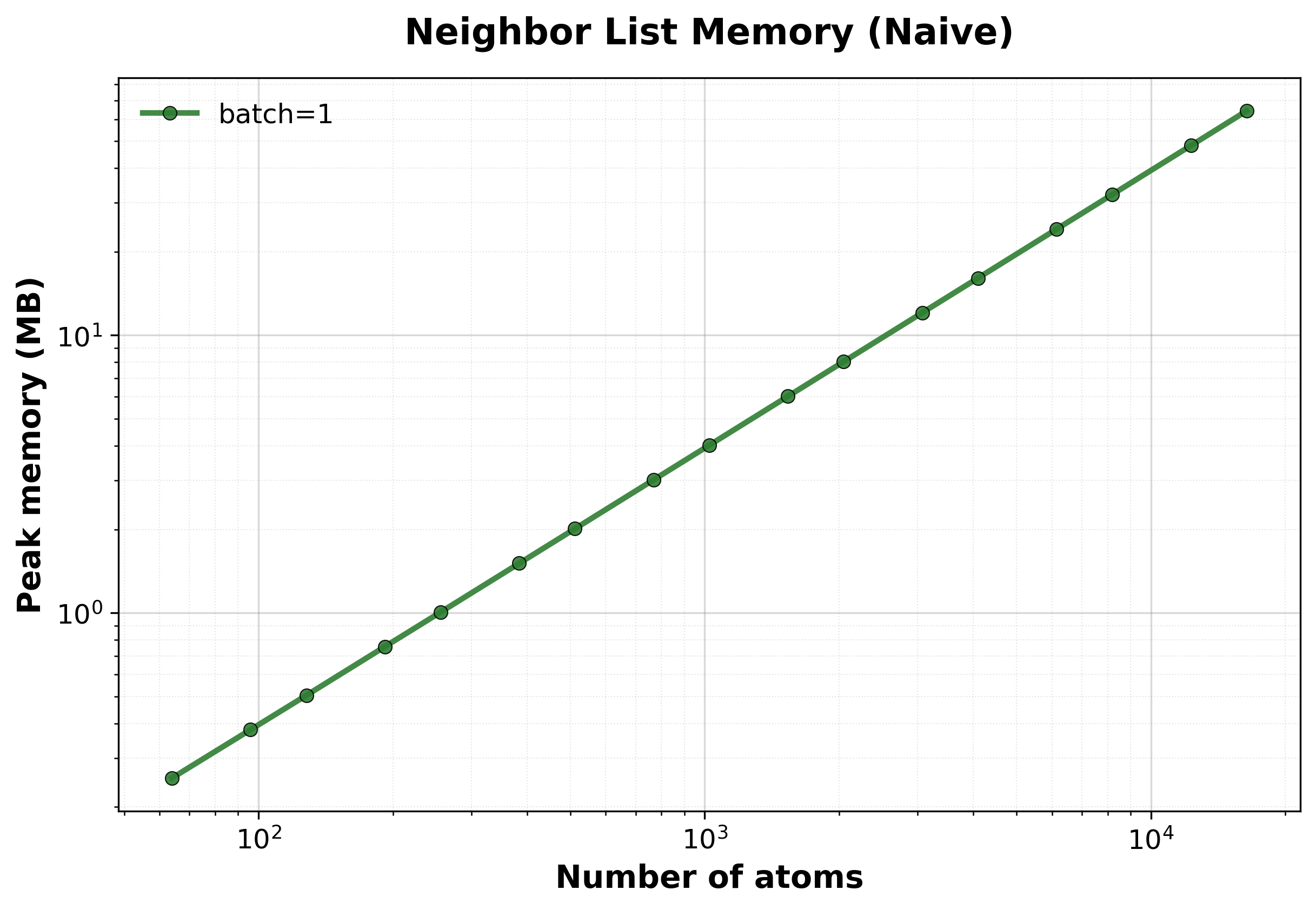
Peak GPU memory consumption vs. system size.#
Spatial hashing \(O(N)\) algorithm. Recommended for medium to large systems where computational efficiency is critical.
Time Scaling
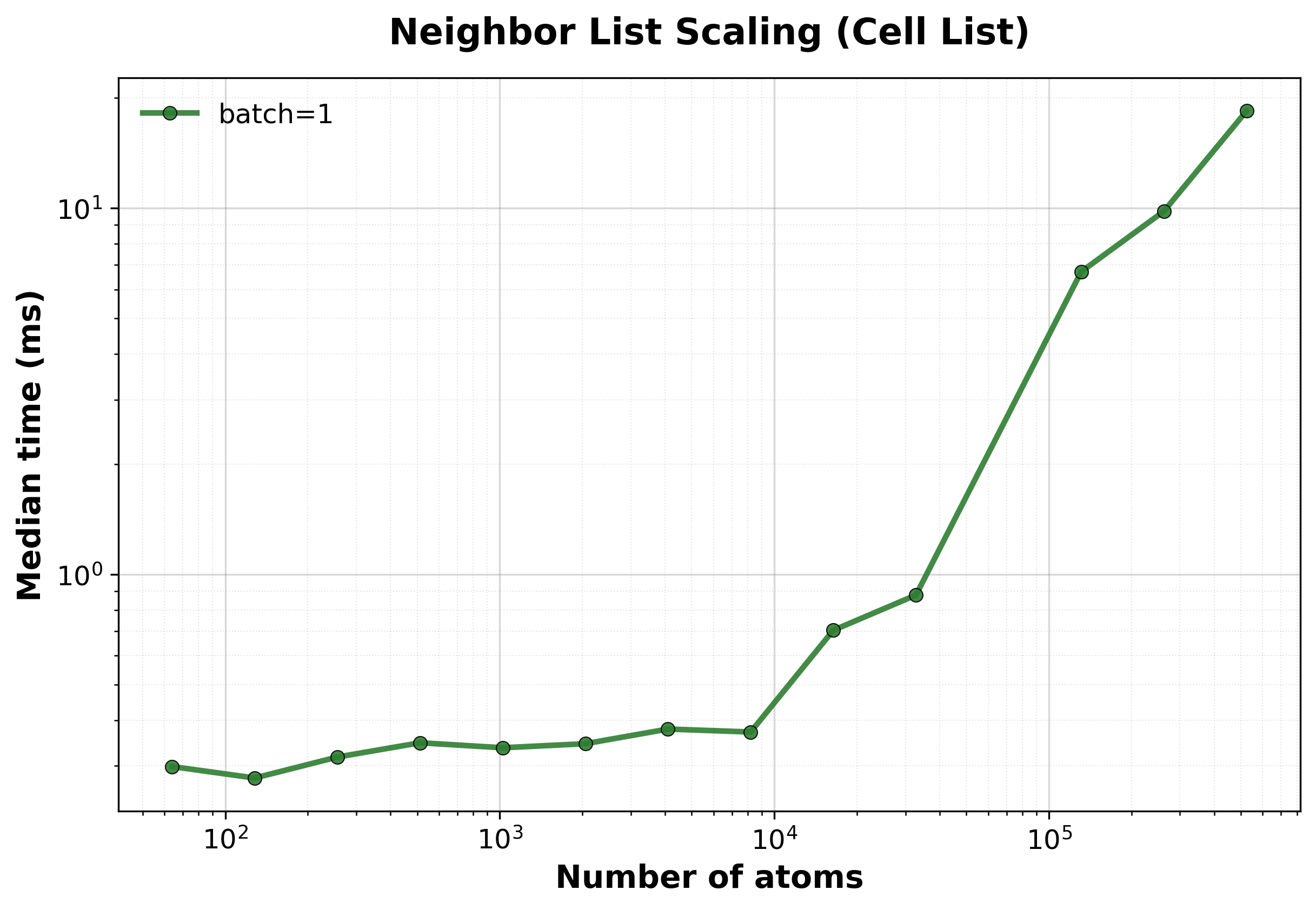
Median execution time vs. system size. Shows near-linear \(O(N)\) scaling for large systems.#
Throughput
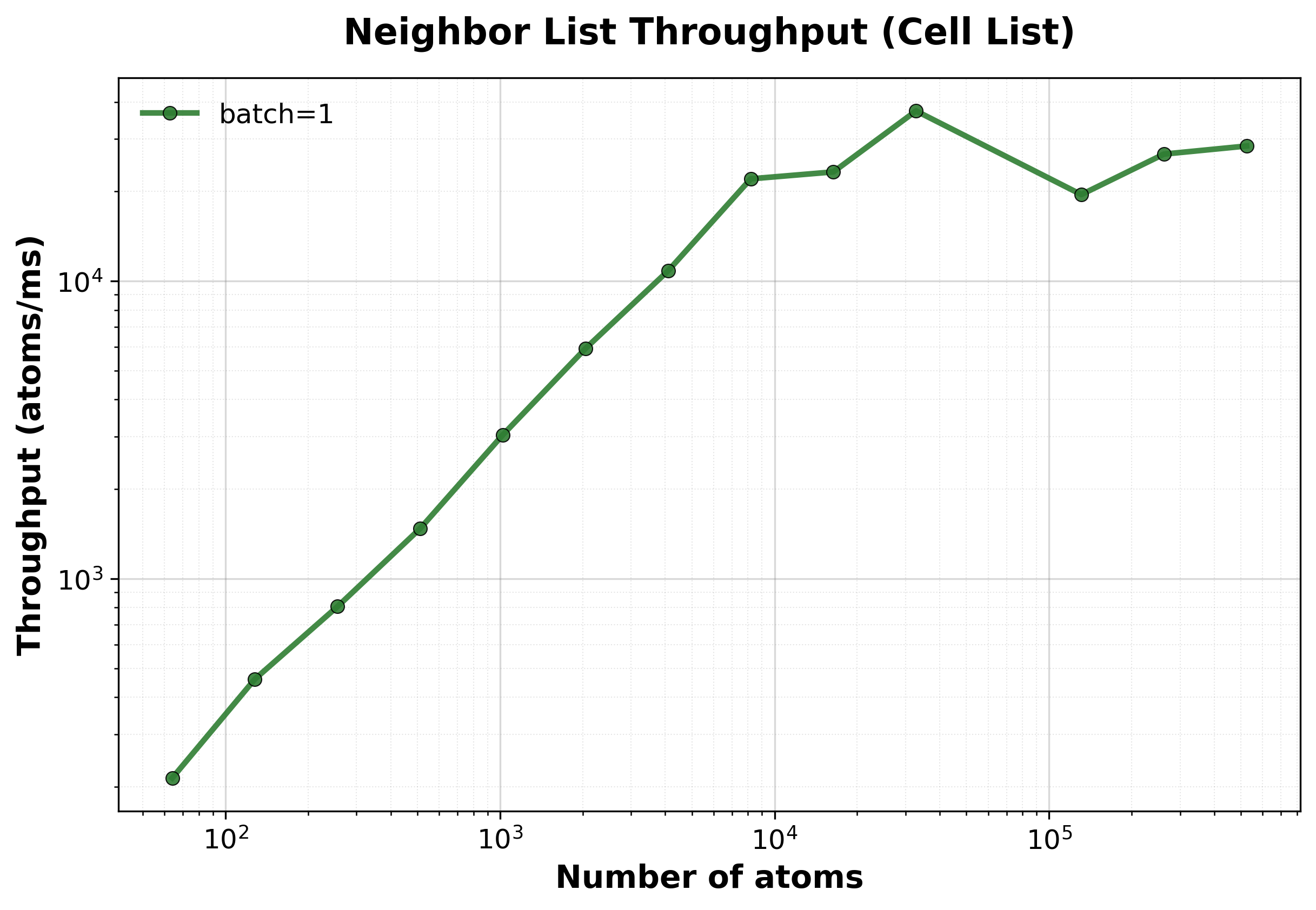
Throughput (atoms/ms) vs. system size. Maintains high throughput even for very large systems.#
Memory Usage
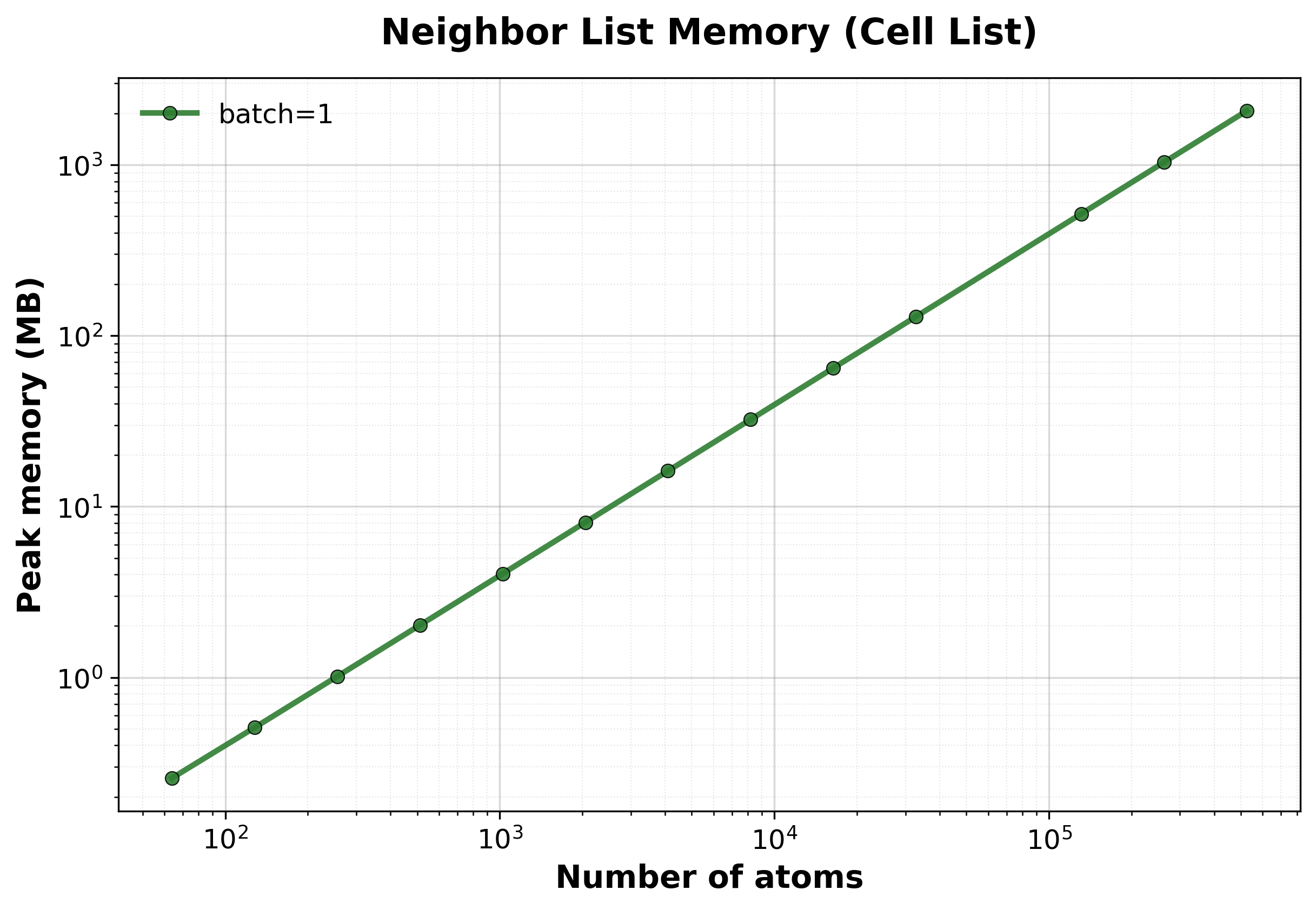
Peak GPU memory consumption vs. system size.#
Batched brute-force algorithm for processing multiple small systems simultaneously. Useful for ML workflows with many small molecules.
Time Scaling
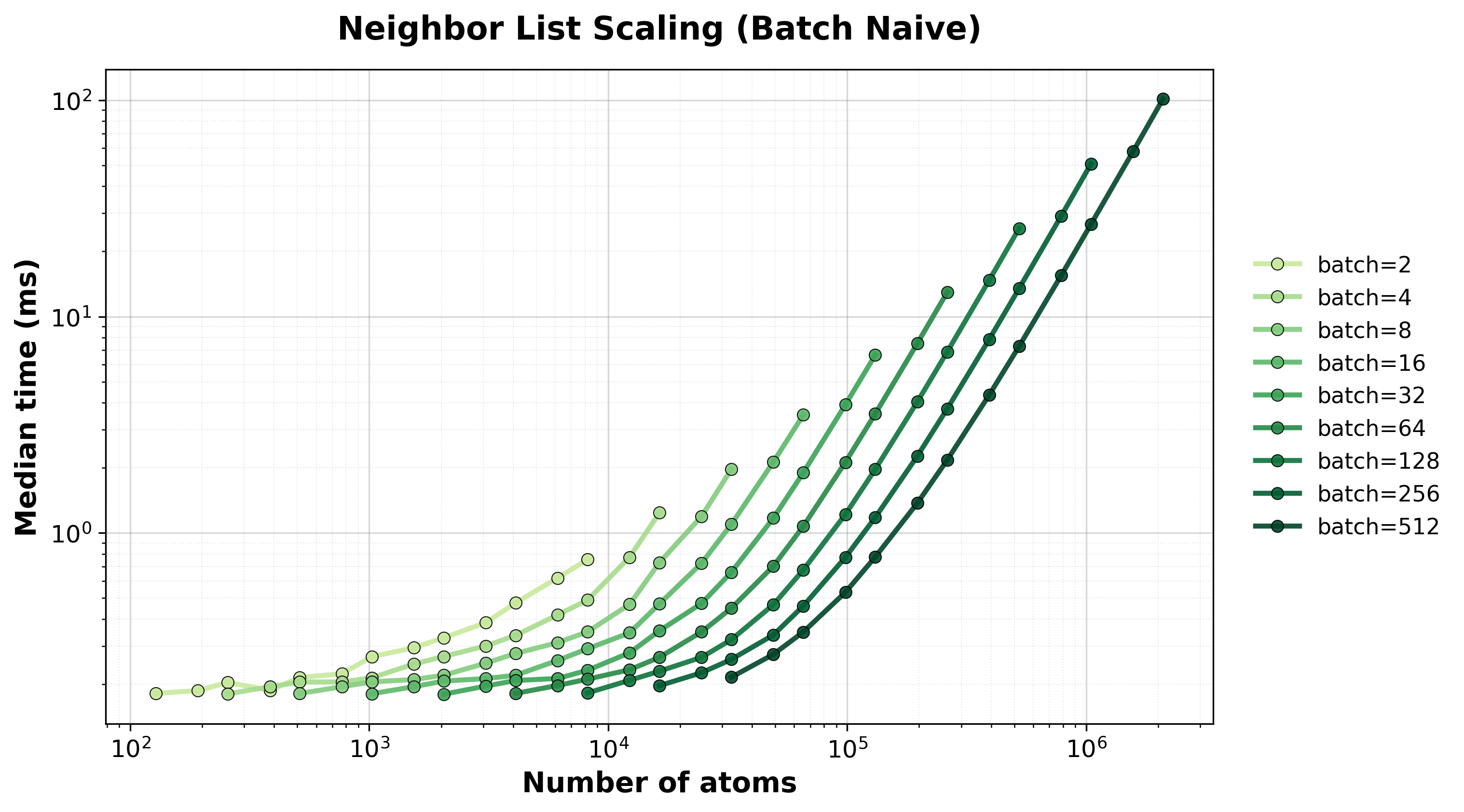
Median execution time vs. total atoms across all batched systems.#
Throughput
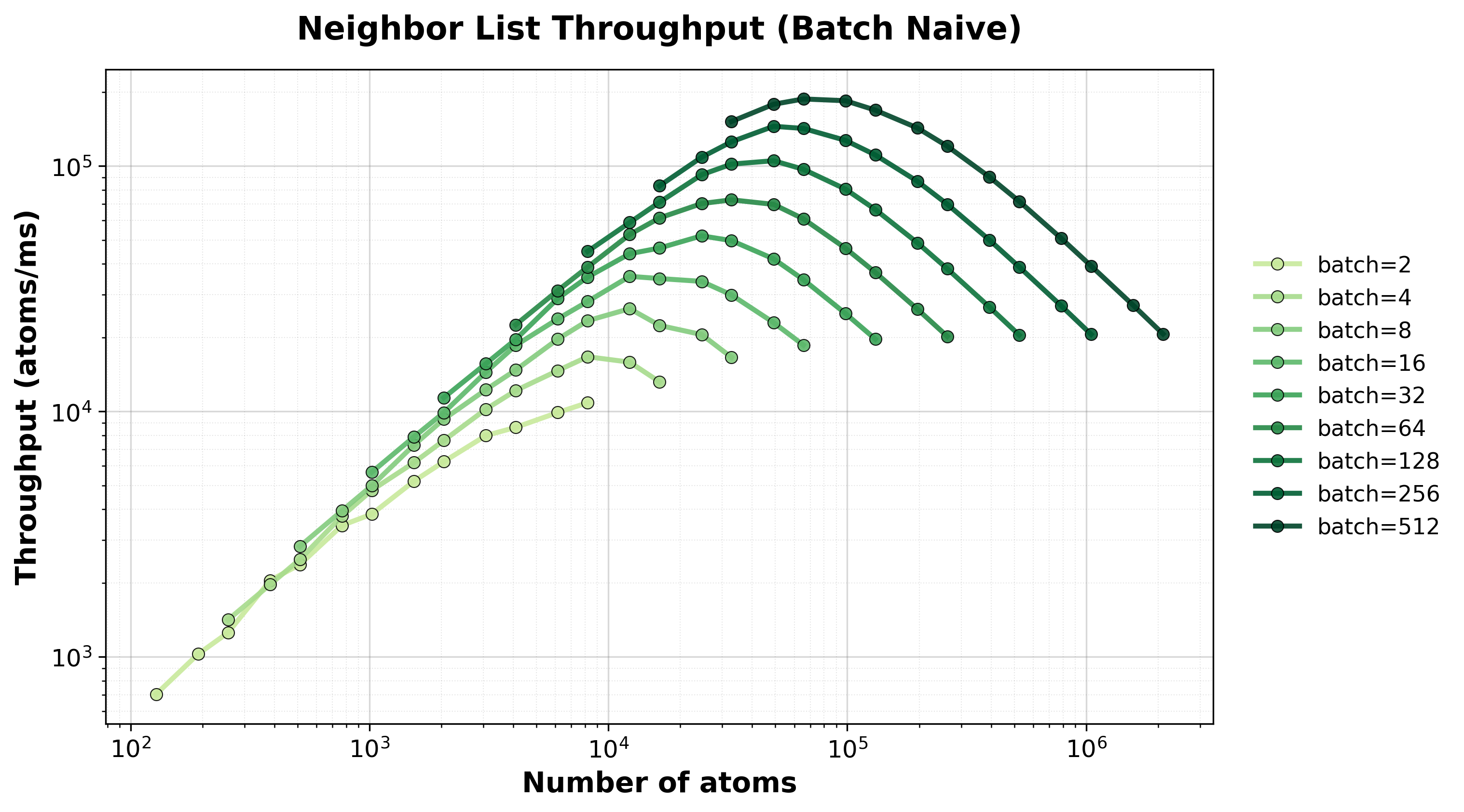
Throughput (atoms/ms) for batched processing. Different lines show different batch sizes.#
Memory Usage
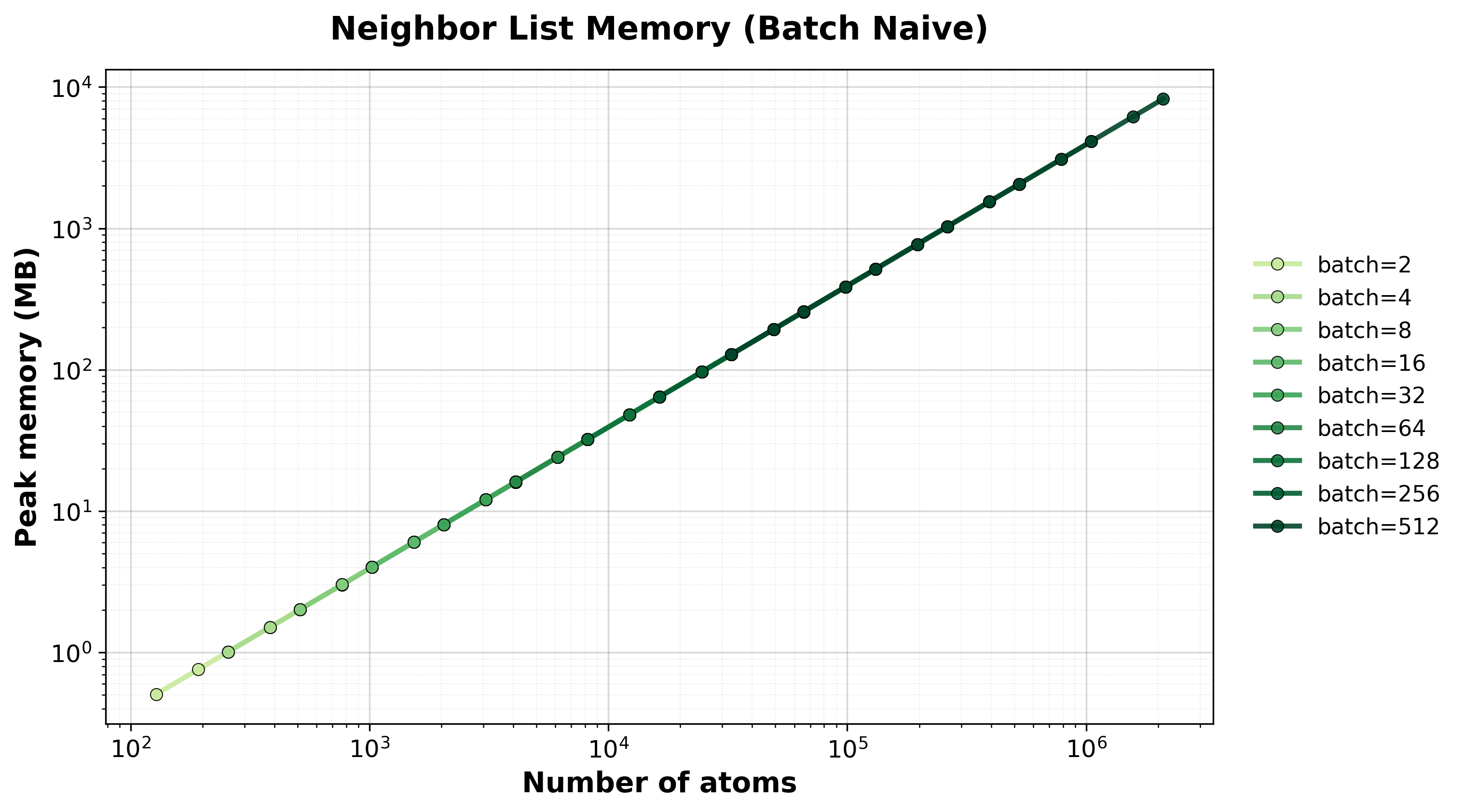
Peak GPU memory consumption for batched systems.#
Batched spatial hashing algorithm for processing multiple systems simultaneously with O(N) scaling per system.
Time Scaling
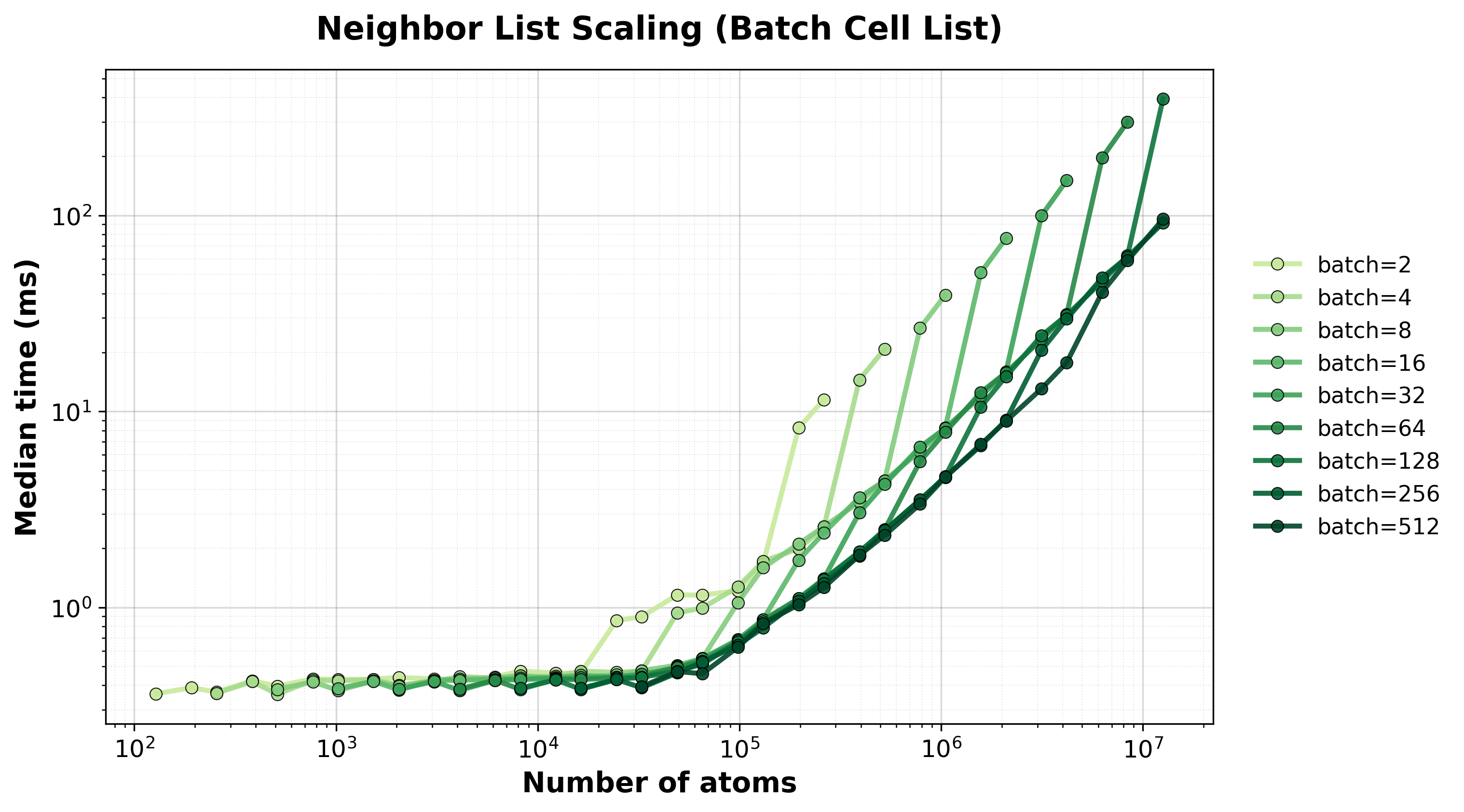
Median execution time vs. total atoms across all batched systems.#
Throughput
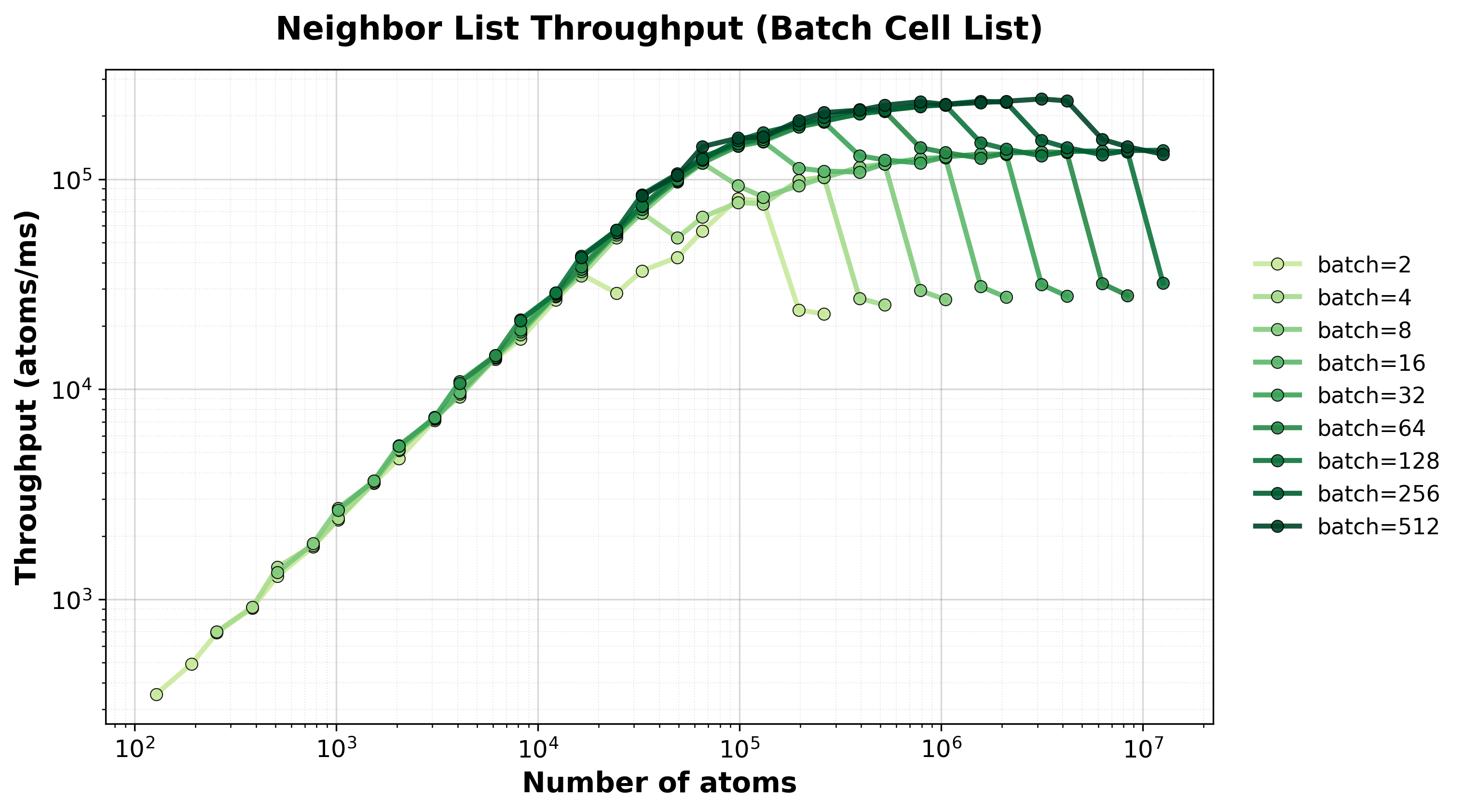
Throughput (atoms/ms) for batched processing. Different lines show different batch sizes.#
Memory Usage
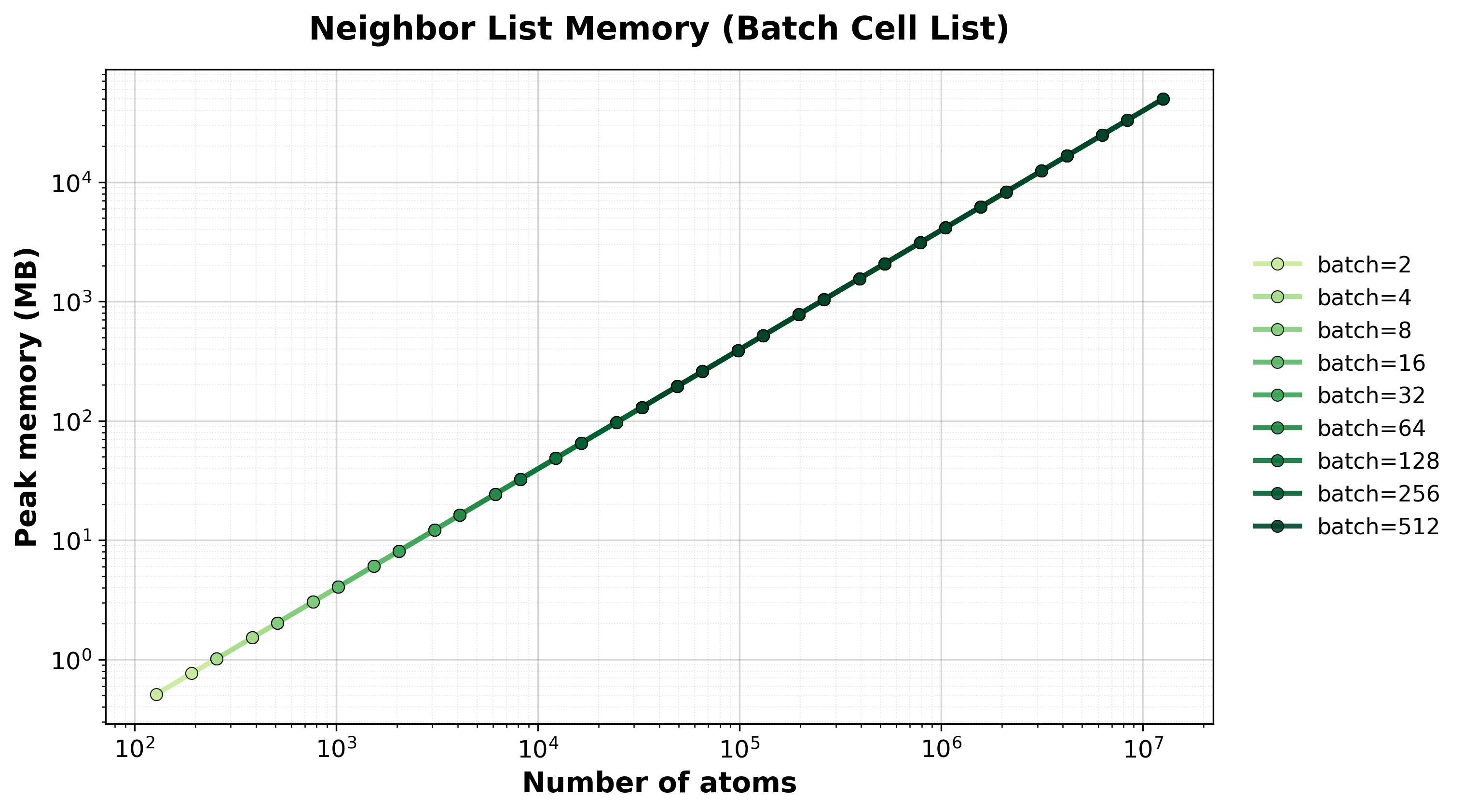
Peak GPU memory consumption for batched systems.#
Hardware Information#
GPU: NVIDIA H100 80GB HBM3
Benchmark Configuration#
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
Cutoff |
5.0 Å |
System Type |
FCC crystal lattice |
Warmup Iterations |
3 |
Timing Iterations |
10 |
Dtype |
|
Interpreting Results#
method
: Algorithm name.
total_atoms
: Total number of atoms in the system.
atoms_per_system
: Atoms per system (relevant for batch methods).
total_neighbors
: Total number of neighbor pairs found.
batch_size
: Number of systems processed simultaneously (1 for non-batch methods).
median_time_ms
: Median execution time in milliseconds (lower is better).
peak_memory_mb
: Peak GPU memory usage in megabytes.
Running Your Own Benchmarks#
To generate benchmark results for your hardware:
cd benchmarks/neighborlist
python benchmark_neighborlist.py \
--config benchmark_config.yaml \
--output-dir ../../docs/benchmarks/benchmark_results
Results will be saved as CSV files and plots will be automatically generated during the next documentation build.
