Speech Recognition¶
Models¶
Currently we support following models:
| Model description | Greedy WER, % | Config file | Checkpoint |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jasper DR 10x5 | 3.61 | jasper10x5_LibriSpeech_nvgrad_masks | link |
| Wave2Letter+ | 6.67 | w2l_plus_large_mp | link |
| DeepSpeech2 | 6.71 | ds2_large_mp | link |
WER is the word error rate obtained on a dev-clean subset of LibriSpeech using
greedy decoder (decoder_params/use_language_model = False).
For the evaluation we used batch_size_per_gpu = 1
to eliminate the effect of cuDNN padding issue.
For more details about model and training parameters, have a look at the configuration files and specific model’s documentation.
Introduction¶
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems can be built using a number of approaches depending on input data type, intermediate representation, model’s type and output post-processing. OpenSeq2Seq is currently focused on end-to-end CTC-based models (like original DeepSpeech model). These models are called end-to-end because they take speech samples and transcripts without any additional information. CTC allows finding an alignment between audio and text. CTC ASR models can be summarized in the following scheme:
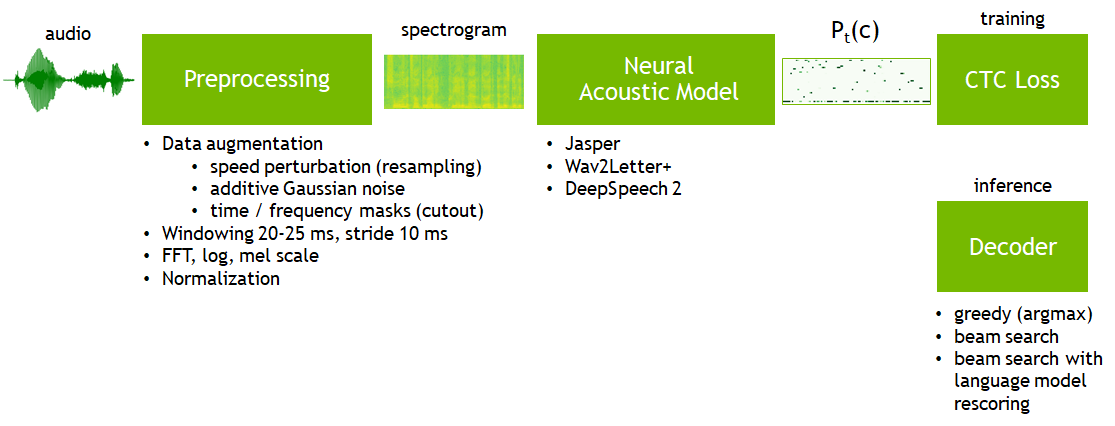
Training pipeline consists of the following blocks:
- audio preprocessing (feature extraction): signal normalization, windowing, (log) spectrogram (or mel scale spectrogram, or MFCC)
- neural acoustic model (which predicts a probability distribution P_t(c) over vocabulary characters c per each time step t given input features per each timestep)
- CTC loss function
Inference pipeline is different for block #3:
- decoder (which transforms a probability distribution into actual transcript)
We support different options for these steps. The recommended pipeline is the following (in order to get the best accuracy, the lowest WER):
- Mel scale log spectrograms for audio features (using librosa backend)
- Jasper as a neural acoustic model
- Baidu’s CTC beam search decoder with N-gram language model rescoring
Note
OpenSeq2Seq has two audio feature extraction backends:
- python_speech_features (psf, it is a default backend for backward compatibility)
- librosa
We recommend to use librosa backend for its numerous important features (e.g., windowing, more accurate mel scale aggregation).
To enable librosa, please make sure that there is a line "backend": "librosa" in "data_layer_params".
Decoders¶
In order to get words out of a trained model one needs to use a decoder. Decoder converts a probability distribution over characters into text. There are two types of decoders that are usually employed with CTC-based models: greedy decoder and beam search decoder with language model re-scoring.
A greedy decoder outputs the most probable character at each time step. It is very fast and it can produce transcripts that are very close to the original pronunciation. But it may introduce many small misspelling errors. Due to the nature of WER metric, even one character error makes a whole word incorrect.
A beam search decoder with language model re-scoring allows checking many possible decodings (beams) at once with assigning a higher score for more probable N-grams according to a given language model. The language model helps to correct misspelling errors. The downside is that it is significantly slower than a greedy decoder.
There are two implementations of beam search decoder in OpenSeq2Seq:
native TensorFlow operation (
./ctc_decoder_with_lm/). It is rather a deprecated decoder due to its slowness (it works in a single CPU thread only). We keep it for backward compatibility. You have to build it (or use pre-built version in NVIDIA TensorFlow container). In order to enable it, you’ll need to define its parameters"beam_width","alpha","beta","decoder_library_path","lm_path","trie_path","alphabet_config_path"and add"use_language_model": Trueline in"decoder_params"section of the config file.Baidu decoder (as a separate Python script). It is parallelized across batch on multiple CPU cores, so it is significantly faster. It doesn’t require a separate trie file as an input. It is the recommended decoder for ASR models. In order to use it, please:
make sure that
"decoder_params"section has'infer_logits_to_pickle': Trueline and that"dataset_files"field of"infer_params"section contains a target CSV filerun inference (to dump logits to a pickle file):
python run.py --mode=infer --config="MODEL_CONFIG" --logdir="MODEL_CHECKPOINT_DIR" --num_gpus=1 --use_horovod=False --decoder_params/use_language_model=False --infer_output_file=model_output.pickle
run beam search decoder (with specific ALPHA, BETA and BEAM_WIDTH hyperparameters):
python scripts/decode.py --logits=model_output.pickle --labels="CSV_FILE" --lm="LM_BINARY" --vocab="ALPHABET_FILE" --alpha=ALPHA --beta=BETA --beam_width=BEAM_WIDTH
It is possible to apply a neural language model (like Transformer-XL) to select the best trascription among all candidates after the beam search. For more details, please see https://github.com/NVIDIA/OpenSeq2Seq/tree/master/external_lm_rescore
Getting started¶
You can start with these instructions to play with a very small model on a toy dataset.
Now let’s consider a relatively lightweight version of DeepSpeech2 based model for English speech recognition on LibriSpeech dataset.
Download and preprocess LibriSpeech dataset:
python scripts/import_librivox.py data/librispeech
Install KenLM:
scripts/install_kenlm.sh
Download and preprocess OpenSLR language model:
scripts/download_lm.sh
Let’s train a small DS2 model.
This model can be trained on 12 GB GPU within a day.
Start training:
python run.py --config_file=example_configs/speech2text/ds2_small_1gpu.py --mode=train_eval
If your GPU does not have enough memory, reduce the batch_size_per_gpu.
Also, you might want to disable evaluation during training by using --mode=train.
In order to get greedy WER metric on validation dataset, please run the following command:
python run.py --config_file=example_configs/speech2text/ds2_small_1gpu.py --mode=eval
If you would like to use beam search decoder with language model re-scoring, please see link
Once training is done (this can take a while on a single GPU), you can run inference:
python run.py --config_file=example_configs/speech2text/ds2_small_1gpu.py --mode=infer --infer_output_file=ds2_out.txt
To train on <N> GPUs without Horovod:
python run.py --config_file=... --mode=train_eval --use_horovod=False --num_gpus=<N>
To train with Horovod on <N> GPUs, use the following command:
mpiexec --allow-run-as-root -np <N> python run.py --config_file=... --mode=train_eval --use_horovod=True